Chlorisondamine diiodide
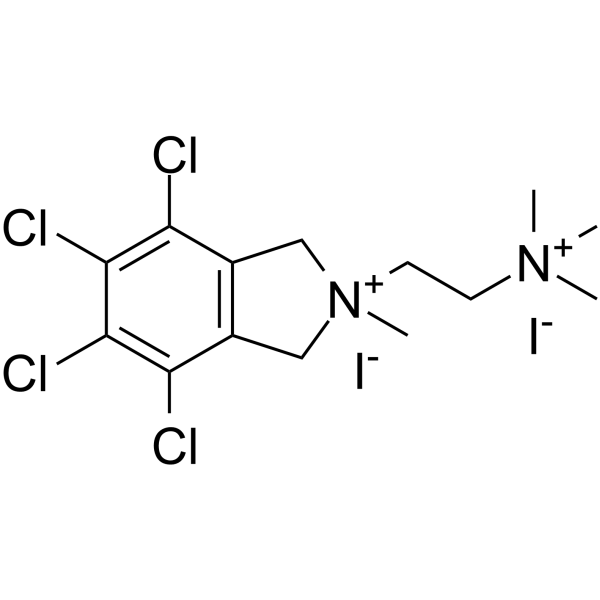
Chlorisondamine diiodide structure
|
Common Name | Chlorisondamine diiodide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 96750-66-2 | Molecular Weight | 611.94 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H20Cl4I2N2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Cardiovascular afferents cause the release of 5-HT in the nucleus tractus solitarii; this release is regulated by the low- (PMAT) not the high-affinity transporter (SERT).
J. Physiol. 593(7) , 1715-29, (2015) The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) integrates inputs from cardiovascular afferents and thus is crucial for cardiovascular homeostasis. These afferents primarily release glutamate, although 5-HT has also been shown to play a role in their actions. Using fast-... |
|
|
Effects of nicotine and chlorisondamine on cerebral glucose utilization in immobilized and freely-moving rats.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 129 , 147-155, (2000) Chlorisondamine blocks central nicotinic receptors for many weeks via an unknown mechanism. Intracerebroventricular administration of [(3)H]-chlorisondamine in rats results in an anatomically restricted and persistent intracellular accumulation of radioactivi... |
|
|
Modulation of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by halothane in rat cortical neurons.
Mol. Pharmacol. 59 , 732-743, (2001) Inhalational general anesthetics have recently been shown to inhibit neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine (ACh) receptors (nnAChRs) expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes and in molluscan neurons. However, drug actions on these systems are not necessarily the same a... |
|
|
Nicotine prevents striatal dopamine loss produced by 6-hydroxydopamine lesion in the substantia nigra.
Brain Res. 888 , 336-342, (2001) While the work of several groups has shown the neuroprotective effects of nicotine in vitro, evidences for the same effects in vivo are controversial, mainly regarding neuroprotection in experimental models of Parkinson's disease. In this context, we investig... |