(+)-TUBOCURARINE CHLORIDE PENTAHYDRATE
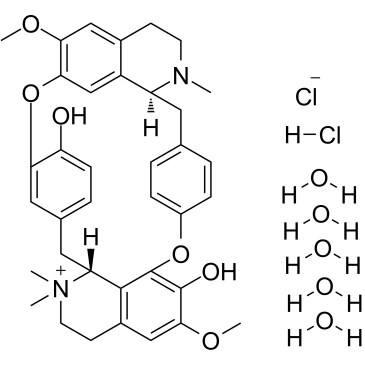
(+)-TUBOCURARINE CHLORIDE PENTAHYDRATE structure
|
Common Name | (+)-TUBOCURARINE CHLORIDE PENTAHYDRATE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6989-98-6 | Molecular Weight | 771.72200 | |
| Density | 1.2074 (rough estimate) | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C37H52Cl2N2O11 | Melting Point | 275-280ºC (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Acetylcholine induces Ca2+ signaling in chicken retinal pigmented epithelial cells during dedifferentiation.
Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 296 , C1195-206, (2009) Retinal pigmented epithelial cells exchange their cellular phenotypes into lens cells and neurons, via depigmented and non-epithelial-shaped dedifferentiated intermediates. Because these dedifferentiated cells can either revert to pigmented epithelial cells o... |
|
|
Interaction of d-tubocurarine analogs with the mouse nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Ligand orientation at the binding site.
J. Biol. Chem. 272 , 24891-24898, (1997) The binding of d-tubocurarine and several of its analogs to the mouse nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) was measured by competition against the initial rate 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin binding to BC3H-1 cells. The changes in affinity due to methylation or h... |
|
|
Acetylcholine receptor inhibition by d-tubocurarine involves both a competitive and a noncompetitive binding site as determined by stopped-flow measurements of receptor-controlled ion flux in membrane vesicles.
Biochemistry 25 , 1786, (1986) The issue of whether d-tubocurarine, the classical acetylcholine receptor inhibitor, inhibits the receptor by a competitive or noncompetitive mechanism has long been controversial. d-Tubocurarine, in this study, has been found to be both a competitive (KC = 1... |
|
|
Proteasome inhibition with bortezomib depletes plasma cells and autoantibodies in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis.
J. Immunol. 186 , 2503-13, (2011) Bortezomib, an inhibitor of proteasomes, has been reported to reduce autoantibody titers and to improve clinical condition in mice suffering from lupus-like disease. Bortezomib depletes both short- and long-lived plasma cells; the latter normally survive the ... |
|
|
Genetic visualization with an improved GCaMP calcium indicator reveals spatiotemporal activation of the spinal motor neurons in zebrafish.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 , 5425-30, (2011) Animal behaviors are generated by well-coordinated activation of neural circuits. In zebrafish, embryos start to show spontaneous muscle contractions at 17 to 19 h postfertilization. To visualize how motor circuits in the spinal cord are activated during this... |
|
|
Chemical communication between regenerating motor axons and Schwann cells in the growth pathway.
Eur. J. Neurosci. 30(3) , 366-75, (2009) There are receptors on denervated Schwann cells that may respond to the neurotransmitters that are released from growth cones of regenerating motor axons. In order to ascertain whether the interaction of the transmitters and their receptors plays a role durin... |
|
|
Effects of non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents on norepinephrine release from human atrial tissue obtained during cardiac surgery.
Br. J. Anaesth. 82 , 904-909, (1999) We have studied the effect of non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents, at concentrations present in serum during anaesthesia, on release of [3H]-norepinephrine ([3H]NE) from superfused atrial appendage obtained during cardiac surgery from 48 patients. ... |
|
|
Neuromuscular activity blockade induced by muscimol and d-tubocurarine differentially affects the survival of embryonic chick motoneurons.
J. Neurosci. 19 , 7925-7939, (1999) To understand better how spontaneous motoneuron activity and intramuscular nerve branching influence motoneuron survival, we chronically treated chicken embryos in ovo with either d-tubocurarine (dTC) or muscimol during the naturally occurring cell death peri... |
|
|
Effects of cholinergic blockers on auditory brain-stem evoked potentials in rats.
J. Neurol. Sci. 164 , 124-128, (1999) The pharmacology of auditory brain-stem evoked potentials (ABEP) pathways is poorly understood. There are anecdotal reports on the involvement of various neurotransmitters but they were not investigated systematically. The aim of this study was to investigate... |