Aminomethyltrioxsalen hydrochloride
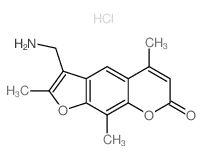
Aminomethyltrioxsalen hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Aminomethyltrioxsalen hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 62442-61-9 | Molecular Weight | 293.74500 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H16ClNO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
In vivo footprint of a picornavirus internal ribosome entry site reveals differences in accessibility to specific RNA structural elements.
J. Gen. Virol. 88(Pt 11) , 3053-62, (2007) Internal ribosome entry site (IRES) elements were described in picornaviruses as an essential region of the viral RNA. Understanding of IRES function requires a detailed knowledge of each step involved in the internal initiation process, from RNA folding and ... |
|
|
'RNA walk' a novel approach to study RNA-RNA interactions between a small RNA and its target.
Nucleic Acids Res. 38(1) , e5, (2010) In this study we describe a novel method to investigate the RNA-RNA interactions between a small RNA and its target that we termed 'RNA walk'. The method is based on UV-induced AMT cross-linking in vivo followed by affinity selection of the hybrid molecules a... |
|
|
Psoralen preparation of antigenically intact noninfectious rotavirus particles.
J. Virol. Methods 38(1) , 93-102, (1992) The use of the synthetic psoralen 4'-aminomethyl-4,5',8-trimethylpsoralen hydrochloride (AMT) is described for the inactivation of infectious rotavirus, a member of the viral family Reoviradae with a double-stranded RNA genome. This method not only provides c... |
|
|
Yeast U1 snRNP-pre-mRNA complex formation without U1snRNA-pre-mRNA base pairing.
RNA 7(1) , 133-42, (2001) Base pairing between the 5' end of U1 snRNA and the conserved 5' splice site of pre-mRNA is important for commitment complex formation in vitro. However, the biochemical mechanisms by which pre-mRNA is initially recognized by the splicing machinery is not wel... |
|
|
Quencher-enhanced specificity of psoralen-photosensitized virus inactivation in platelet concentrates.
Transfusion 34(9) , 802-10, (1994) Treatment with psoralens and UVA (PUVA) has been shown to be efficacious in eliminating the risk of virus transmission by platelet concentrates (PCs). It has previously been demonstrated that, during the inactivation of cell-free vesicular stomatitis virus (V... |
|
|
Effects of hydroxyl radical scavengers on relaxation of supercoiled DNA by aminomethyl-trimethyl-psoralen and monochromatic UVA photons.
Free Radic. Biol. Med. 20(5) , 751-6, (1996) The ability of scavengers of hydroxyl radical (OH radical) to modulate the photosensitized relaxation (induction of the first single-strand break) of supercoiled plasmid DNA with UVA photoactivated 4'-aminomethyl-4,5',8-trimethylpsoralen was examined by compa... |
|
|
Elimination of cytokine production in stored platelet concentrate aliquots by photochemical treatment with psoralen plus ultraviolet A light.
Transfusion 39(3) , 239-48, (1999) Cytokines generated in platelet concentrates (PCs) during storage have been implicated as possible mediators of febrile nonhemolytic transfusion reactions. Two potential methods of white cell inactivation were compared for their ability to reduce cytokine syn... |
|
|
Determination of residual 4'-aminomethyl-4,5',8-trimethylpsoralen and mutagenicity testing following psoralen plus UVA treatment of platelet suspensions.
Photochem. Photobiol. 57(5) , 819-24, (1993) Psoralens and UVA light have been used in the laboratory to study the inactivation of viruses that may be infrequently present in platelet concentrates that are prepared for transfusion. In order to evaluate safety aspects of the treatment of platelet suspens... |
|
|
Inactivation of Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigote forms in blood components with a Psoralen and Ultraviolet A light.
Photochem. Photobiol. 63(5) , 562-5, (1996) Inactivation of the blood-borne parasite Trypanosoma cruzi by UVA and 4'-aminomethyl-4,5',8-trimethylpsoralen (AMT) was studied in the blood components fresh frozen plasma (FFP) and platelet concentrate (PC). The AMT was utilized at a concentration of 50 micr... |
|
|
Inactivation of free and cell-associated human immunodeficiency virus in platelet suspensions by aminomethyltrimethylpsoralen and ultraviolet light.
Transfusion 34(8) , 680-4, (1994) It has previously been reported that 40 micrograms per mL of aminomethyltrimethylpsoralen (AMT) plus 2.4 to 7.2 J per cm2 of ultraviolet A (UVA) light inactivated 4 to 6 log10 of several model viruses in platelet suspensions. This inactivation was achieved wh... |