Nedocromil
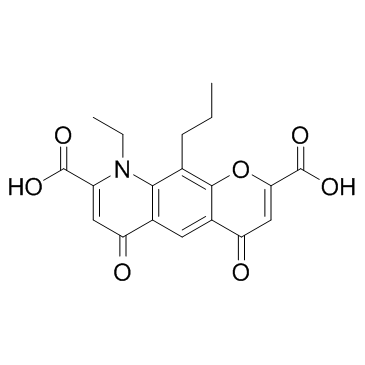
Nedocromil structure
|
Common Name | Nedocromil | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 69049-73-6 | Molecular Weight | 371.341 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 645.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H17NO7 | Melting Point | 299ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 344.2±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Estrogen inhibits mast cell chymase release to prevent pressure overload-induced adverse cardiac remodeling.
Hypertension 65(2) , 328-34, (2015) Estrogen regulation of myocardial chymase and chymase effects on cardiac remodeling are unknown. To test the hypothesis that estrogen prevents pressure overload-induced adverse cardiac remodeling by inhibiting mast cell (MC) chymase release, transverse aortic... |
|
|
Diagnostic accuracy of the bronchodilator response in children.
J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 132(3) , 554-559.e5, (2013) The bronchodilator response (BDR) reflects the reversibility of airflow obstruction and is recommended as an adjunctive test to diagnose asthma. The validity of the commonly used definition of BDR, a 12% or greater change in FEV1 from baseline, has been quest... |
|
|
This asthma treatment has a lasting side effect in children.
J. Fam. Pract. 62(9) , 500-2, (2013) A new study finds that when children with asthma use inhaled corticosteroids, the effect on growth may not be temporary, as once thought. |
|
|
Corticosteroid use and bone mineral accretion in children with asthma: Effect modification by vitamin D
J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 130(1) , 53-60.e4, (2012) Background The adverse effects of corticosteroids on bone mineral accretion (BMA) have been well documented. Vitamin D insufficiency, a prevalent condition in the pediatric population, has also been associated with decreased bone mineral density (BMD). |
|
|
Chloride transport and the actions of nedocromil sodium and cromolyn sodium in asthma.
J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 98(5 Pt 2) , S102-5; discussion S105-6, (1996) Nedocromil sodium has been shown to be capable of inhibiting chloride ion flux in mast cells, epithelial cells, and neurons. This feature may explain how it can prevent responses such as mast-cell degranulation, the effects of osmolarity changes in the airway... |
|
|
Cromoglycate drugs suppress eicosanoid generation in U937 cells by promoting the release of Anx-A1.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 77(12) , 1814-26, (2009) Using biochemical, epifluorescence and electron microscopic techniques in a U937 model system, we investigated the effect of anti-allergic drugs di-sodium cromoglycate and sodium nedocromil on the trafficking and release of the anti-inflammatory protein Annex... |
|
|
Nedocromil sodium: a review of the evidence for a dual mechanism of action.
Clin. Exp. Allergy 30(4) , 461-8, (2000)
|
|
|
An essential role for mast cells as modulators of neutrophils influx in collagen-induced arthritis in the mouse.
Lab. Invest. 91(1) , 33-42, (2011) Mast cells are involved in immune disorders so that many of the proinflammatory and tissue destructive mediators produced by these cells have been implicated in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. This scenario prompted us to investigate the correlation... |
|
|
Antiallergic cromones inhibit neutrophil recruitment onto vascular endothelium via annexin-A1 mobilization.
Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 30(9) , 1718-24, (2010) To determine whether the inhibitory action of the antiallergic cromone "mast cell stabilizing" drugs on polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) trafficking is mediated through an annexin-A1 (Anx-A1) dependent mechanism.Intravital microscopy was used to monitor the ... |
|
|
Anti-allergic cromones inhibit histamine and eicosanoid release from activated human and murine mast cells by releasing Annexin A1.
PLoS ONE 8(3) , e58963, (2013) Although the 'cromones' (di-sodium cromoglycate and sodium nedocromil) are used to treat allergy and asthma, their 'mast cell stabilising' mechanism of pharmacological action has never been convincingly explained. Here, we investigate the hypothesis that thes... |