BW A868C
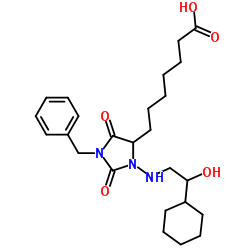
BW A868C structure
|
Common Name | BW A868C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 118675-50-6 | Molecular Weight | 459.578 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 638.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H37N3O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 339.7±34.3 °C | |
|
Multiplexed phosphospecific flow cytometry enables large-scale signaling profiling and drug screening in blood platelets.
J. Thromb. Haemost. 12(10) , 1733-43, (2014) Dissecting the signaling events that contribute to platelet activation will increase our understanding of platelet function and aid in the development of new antiplatelet agents. However, high-throughput methodology for the quantitative analysis of platelet s... |
|
|
Genetic validation of a therapeutic target in a mouse model of ALS.
Sci. Transl. Med. 6(248) , 248ra104, (2014) Neurons produced from stem cells have emerged as a tool to identify new therapeutic targets for neurological diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). However, it remains unclear to what extent these new mechanistic insights will translate to anim... |
|
|
Pro-migratory actions of the prostacyclin receptor in human breast cancer cells that over-express cyclooxygenase-2.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 96 , 306-14, (2015) Metastasis is the major cause of death in cancer patients. Elevated expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is observed in many human cancers and over-production of downstream prostaglandins (PGs) has been shown to stimulate metastasis. A role for increased PG... |
|
|
Interactive effect of histamine and prostaglandin D2 on nasal allergic symptoms in rats.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 554(2-3) , 229-34, (2007) This study was undertaken to investigate the interactive effect of histamine and prostaglandin D(2) in nasal allergic symptoms in rats. The intranasal application of histamine at doses lower than 10 mumol/site caused no sneezing or nasal rubbing. In addition,... |
|
|
Induction of apoptosis in non-small cell lung carcinoma A549 cells by PGD₂ metabolite, 15d-PGJ₂.
Cell Biol. Int. 35(11) , 1089-96, (2011) PGD2 (prostaglandin D2) is a mediator in various pathophysiological processes, including inflammation and tumorigenesis. PGD2 can be converted into active metabolites and is known to activate two distinct receptors, DP (PGD2 receptor) and CRTH2/DP2 (chemoattr... |
|
|
Prostaglandin DP receptors positively coupled to adenylyl cyclase in embryonic bovine tracheal (EBTr) cells: pharmacological characterization using agonists and antagonists.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 127 , 204, (1999) Various prostaglandin agonists representing various classes of receptor subtypes were evaluated for their ability to stimulate adenylyl cyclase via the endogenous DP receptor in embryonic bovine tracheal (EBTr) cells. Two antagonists were used to block the ag... |
|
|
GIF-0173 protects against cerebral infarction through DP1 receptor activation.
Exp. Neurol. 219(2) , 481-91, (2009) The neuroprotective effects and mechanism of action of GIF-0173, a Delta12-prostaglandin J analogue, were investigated in the early phase of cerebral ischemia. GIF-0173 was administered intravenously immediately following middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCA... |
|
|
A functional study on prostanoid receptors involved in cultured human iridal melanocyte stimulation.
Exp. Eye Res. 73(1) , 93-100, (2001) The effects of various prostanoids on the growth, melanogenesis and dendrification of cultured iridal melanocytes were studied. Iridal melanocytes were isolated and cultured with medium supplemented with cAMP elevating agents and basic fibroblast growth facto... |
|
|
CRTH2 is not involved in the anti-enteropooling effect of PGD2 in the small intestine.
Pharmacology 81(3) , 236-40, (2008) The majority of prostaglandins (PGs) are known to induce intestinal fluid secretion (enteropooling). In contrast, PGD(2) has been demonstrated to inhibit fluid secretion induced by other PGs. This study was aimed to investigate, by the use of selective agonis... |
|
|
PGD2 induces eotaxin-3 via PPARγ from sebocytes: a possible pathogenesis of eosinophilic pustular folliculitis.
J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 129(2) , 536-43, (2012) Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis (EPF) is a chronic intractable pruritic dermatosis characterized by massive eosinophil infiltrates involving the pilosebaceous units. Recently, EPF has been regarded as an important clinical marker of HIV infection, and its ... |