| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
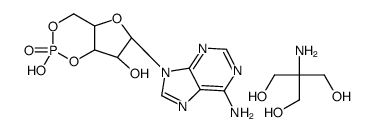 |
ADENOSINE 3':5'-CYCLIC MONOPHOSPHATE TRIS SALT
CAS:102029-77-6 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Glucose
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
 |
Retinoic acid
CAS:302-79-4 |
|
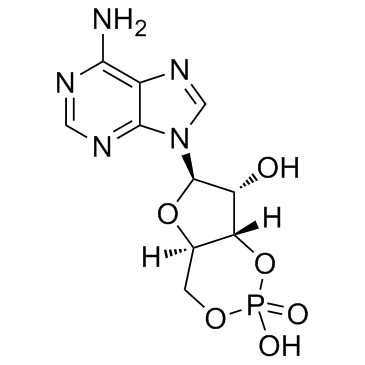 |
Adenosine cyclophosphate
CAS:60-92-4 |
|
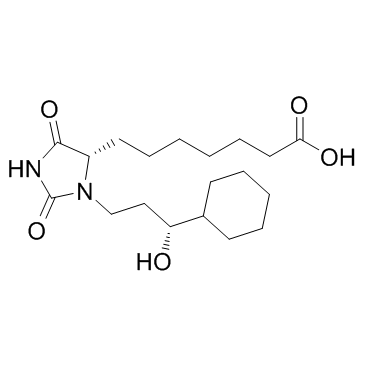 |
BW 245C
CAS:72814-32-5 |
|
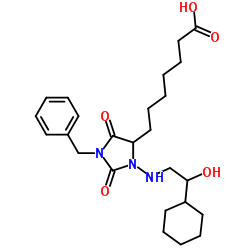 |
BW A868C
CAS:118675-50-6 |