ADENOSINE 3':5'-CYCLIC MONOPHOSPHATE TRIS SALT
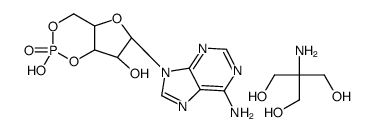
ADENOSINE 3':5'-CYCLIC MONOPHOSPHATE TRIS SALT structure
|
Common Name | ADENOSINE 3':5'-CYCLIC MONOPHOSPHATE TRIS SALT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 102029-77-6 | Molecular Weight | 450.34100 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H23N6O9P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Sinensetin enhances adipogenesis and lipolysis by increasing cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38(4) , 552-8, (2015) Sinensetin is a rare polymethoxylated flavone (PMF) found in certain citrus fruits. In this study, we investigated the effects of sinensetin on lipid metabolism in 3T3-L1 cells. Sinensetin promoted adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes growing in incomplete di... |
|
|
Suppression of InsP3 receptor-mediated Ca2+ signaling alleviates mutant presenilin-linked familial Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis.
J. Neurosci. 34(20) , 6910-23, (2014) Exaggerated intracellular Ca(2+) signaling is a robust proximal phenotype observed in cells expressing familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD)-causing mutant presenilins (PSs). The mechanisms that underlie this phenotype are controversial and their in vivo relevan... |
|
|
Prostacyclin receptor expression on platelets of humans with type 2 diabetes is inversely correlated with hemoglobin A1c levels.
Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 116-117 , 131-5, (2015) Inappropriate platelet aggregation can result in thrombosis and tissue ischemia. When compared to healthy human platelets, those of humans with type 2 diabetes (DM2) exhibit increased aggregation when stimulated. Activation of the platelet prostacyclin recept... |
|
|
The regions within the N-terminus critical for human glucagon like peptide-1 receptor (hGLP-1R) cell surface expression.
Sci. Rep. 4 , 7410, (2014) The hGLP-1R is a target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and belongs to the class B family of GPCRs. Like other class B GPCRs, the GLP-1R contains an N-terminal signal peptide (SP) and undergoes N-linked glycosylation, which are important for its traffick... |
|
|
PKA signaling drives mammary tumorigenesis through Src.
Oncogene 34(9) , 1160-73, (2015) Protein kinase A (PKA) hyperactivation causes hereditary endocrine neoplasias; however, its role in sporadic epithelial cancers is unknown. Here, we show that heightened PKA activity in the mammary epithelium generates tumors. Mammary-restricted biallelic abl... |
|
|
Development of a FRET biosensor with high specificity for Akt.
Cell Struct. Funct. 39(1) , 9-20, (2014) The serine/threonine kinase Akt plays a critical role in cell proliferation, survival, and tumorigenesis. As a central kinase in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway, its activation mechanism at the plasma membrane has been well characterized. However, t... |
|
|
Inhibition of the GTPase Rac1 mediates the antimigratory effects of metformin in prostate cancer cells.
Mol. Cancer Ther. 14(2) , 586-96, (2015) Cell migration is a critical step in the progression of prostate cancer to the metastatic state, the lethal form of the disease. The antidiabetic drug metformin has been shown to display antitumoral properties in prostate cancer cell and animal models; howeve... |
|
|
Ram seminal plasma proteins contribute to sperm capacitation and modulate sperm-zona pellucida interaction.
Theriogenology 83(4) , 670-8, (2015) Incubation of ram spermatozoa in capacitating conditions with cAMP-elevating agents promotes a progressive time-dependent increase in the capacitated sperm subpopulation. In this study, the fertilizing capacity of ram spermatozoa (ability to bind to the zona ... |
|
|
Combined treatment with ABT-737 and VX-680 induces apoptosis in Bcl-2- and c-FLIP-overexpressing breast carcinoma cells.
Oncol. Rep. 33(3) , 1395-401, (2015) ABT-737, a BH3-mimetic small-molecule inhibitor, binds with very high affinity to Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and Bcl-w, and inhibits their activity. Aurora kinase is one of the serine/threonine kinase family members and is a vital and critical regulator of mitosis and mei... |
|
|
Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits cell cycle activity of embryonic cardiac progenitor cells via its NPRA receptor signaling axis.
Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 308(7) , C557-69, (2015) The biological effects of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) are mediated by natriuretic peptide receptors (NPRs), which can either activate guanylyl cyclase (NPRA and NPRB) or inhibit adenylyl cyclase (NPRC) to modulate intracellular cGMP or cAMP, respectively... |