Valeronitrile
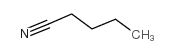
Valeronitrile structure
|
Common Name | Valeronitrile | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 110-59-8 | Molecular Weight | 83.13170 | |
| Density | 0.795 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 139-141 °C(lit.) | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9N | Melting Point | −96 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 105 °F | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Novel organic solvents for electrochemistry at the liquid/liquid interface.
Analyst 140(6) , 1947-54, (2015) Two-phase voltammetry has been carried out using a reverse cell configuration, i.e. with the lower density organic solvent on the top of the aqueous solution in the cell, where the organic solvents contain either nitrile or ketone functional groups. The trans... |
|
|
Molecularly imprinted polymers for cleanup and selective extraction of curcuminoids in medicinal herbal extracts.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407(3) , 803-12, (2015) This paper describes the synthesis of novel molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs), prepared by a noncovalent imprinting approach, for cleanup and preconcentration of curcumin (CUR) and bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDMC) from medicinal herbal extracts and further ana... |
|
|
Anatase TiO2 Nanoparticles with Exposed {001} Facets for Efficient Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 12143, (2015) Anatase TiO2 nanoparticles with exposed {001} facets were synthesized from Ti powder via a sequential hydrothermal reaction process. At the first-step hydrothermal reaction, H-titanate nanowires were obtained in NaOH solution with Ti powder, and at second-ste... |
|
|
In vitro metabolic conversion of the organic breakdown products of glucosinolate to goitrogenic thiocyanate anion.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95 , 2244-51, (2015) Glucosinolates are abundant in Brassicaceae vegetables, and they are degraded into various organic breakdown products (BPs) (R-CN, -NCS and -SCN) by myrosinase when plant tissues are damaged. This study was designed to investigate whether these BPs could be b... |
|
|
High-performance electrocatalysis using metallic cobalt pyrite (CoS₂) micro- and nanostructures.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(28) , 10053-61, (2014) The development of efficient and robust earth-abundant electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) is an ongoing challenge. We report metallic cobalt pyrite (cobalt disulfide, CoS2) as one such high-activity candidate material and demonstrate t... |
|
|
Molecularly imprinted polymer beads for clean-up and preconcentration of β-lactamase-resistant penicillins in milk.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 408 , 1843-54, (2016) This work describes the development and application of class-selective molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) for the analysis of beta-lactamase-resistant penicillins, namely cloxacillin (CLOXA), oxacillin (OXA), and dicloxacillin (DICLOXA), in milk samples. O... |
|
|
Valeronitrile hydrolysis in supercritical water.
ChemSusChem 3(1) , 85-90, (2010) Nitriles act as important intermediates for the chemical industry and are accessible on a large scale through hydrocyanation or ammonoxidation. Nitrile hydrolysis yields amides and acids used in various applications. The conventional nitrile hydrolysis proces... |
|
|
Homogeneous catalysis of valeronitrile hydrolysis under supercritical conditions.
ChemSusChem 5(1) , 200-5, (2012) Supercritical nitrile hydrolysis can be used for both, amide and acid production as well as waste water treatment, as the hydrolysis products show good biodegradability. The conventional process at ambient conditions requires large amounts of mineral acid or ... |
|
|
Enhanced performance of dye-sensitized solar cells with dual-function coadsorbent: reducing the surface concentration of dye-iodine complexes concomitant with attenuated charge recombination.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17 , 22985-90, (2015) In this paper, we have investigated the effects of oleic acid as a dual-function coadsorbent on recombination and iodine binding in dye-sensitized solar cells. Oleic acid as a dual-function coadsorbent effectively shields the back electron transfer from TiO2 ... |
|
|
Cellular uptake and intracellular degradation of poly(alkyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles.
J. Nanobiotechnology 14 , 1, (2016) Poly(alkyl cyanoacrylate) (PACA) nanoparticles have shown promise as drug carriers both to solid tumors and across the blood-brain barrier. Efficient drug delivery requires both high cellular uptake of the nanoparticles and release of the drug from the nanopa... |