Haloxon
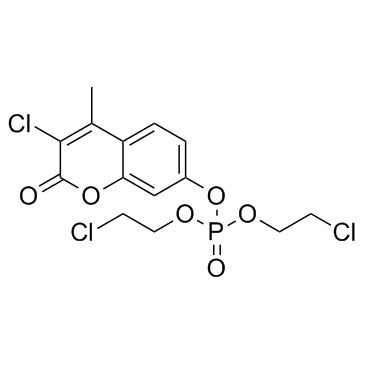
Haloxon structure
|
Common Name | Haloxon | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 321-55-1 | Molecular Weight | 415.59000 | |
| Density | 1.5g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 504.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H14Cl3O6P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 438.8ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Effects of selected organophosphate insecticides on serum cholinesterase isoenzyme patterns in the rat.
Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 38(3) , 196-9, (1996) The serum cholinesterase (ChE) isoenzyme in rats shows 6 bands after polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis. The effects of organophosphates (fenthion, chlorpyrifos, diazinon, bromophos, propaphos, haloxon, and DFP) on serum ChE isoenzyme bands were stud... |
|
|
Effect of some anthelmintics on malate dehydrogenase activity and mortality in two avian nematodes Ascaridia galli and Heterakis gallinae.
Angew. Parasitol. 27(3) , 175-80, (1986) Cambendazole and tiabendazole at 10(-4) M concentrations caused mortality in both the parasites after 10 min and 20 min, respectively. H. gallinae was killed by 10(-4) M haloxon but A. galli remained alive even after 60 min exposure. The effect of these drugs... |
|
|
Effect of cambendazole and haloxon on the carbohydrate metabolism of Ascaridia galli and Heterakis gallinae (Nematoda).
Angew. Parasitol. 31(2) , 101-5, (1990) Cambendazole 10(-4) M significantly reduced the level of glycogen in both the parasites. Lactic acid level was found enhanced. Oxygen consumption was suppressed by 63 and 94% in A. galli and H. gallinae, respectively, by 10(-4) M cambendazole. Haloxon did not... |
|
|
Haloxon: critical tests of antiparasitic activity in equids.
Am. J. Vet. Res. 42(6) , 1043-5, (1981) Critical tests were conducted in 14 naturally infected equids (13 horses and 1 pony) to evaluate the antiparasitic activity of haloxon. Single doses were administered by stomach tube to 3 horses and 1 pony (60 mg/kg of body weight), by addition to the feed of... |
|
|
Haloxon poisoning in geese.
Vet. Rec. 107(23) , 541, (1980)
|
|
|
Structure-inhibition relationships in the interaction of butyrylcholinesterase with bambuterol, haloxon and their leaving groups.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 157-158 , 421-3, (2005)
|
|
|
Laryngeal paralysis in Arabian foals associated with oral haloxon administration.
Equine Vet. J. 13(3) , 171-6, (1981) Bilateral laryngeal paralysis is described in 5 Arabian and part-Arabian foals aged between 23 and 35 days. Tracheotomies resulted in complete relief of dyspnoea. Two cases showed recovery of abductor function of the right arytenoid cartilage after 3 weeks an... |
|
|
Anthelmintics for cattle.
Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2(2) , 489-501, (1986) A number of anthelmintics are available for the control of gastrointestinal nematodes in cattle. In North America, O. ostertagi, Cooperia spp., lung worm, and F. hepatica probably cause the greatest losses in production. The older anthelmintics are often defi... |
|
|
Role of the peripheral anionic site on acetylcholinesterase: inhibition by substrates and coumarin derivatives.
Mol. Pharmacol. 39(1) , 98-104, (1991) Propidium has been demonstrated in previous studies to be a selective ligand for the peripheral anionic site on acetylcholinesterase (EC 3.1.1.7). Its association with this site can be advantageously monitored by direct fluorescent titration. We have measured... |
|
|
Binding sites on acetylcholinesterase for reversible ligands and phosphorylating agents. A theoretical model tested on haloxon and phosphostigmine.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 33(4) , 671-7, (1984) The reaction of acetylcholinesterase (EC 3.1.1.7; human erythrocytes) with phosphostigmine, haloxon and VX was studied, and the effect of three reversible ligands (TMA, edrophonium, coumarin) and of acetylthiocholine upon the time-dependent and time-independe... |