1-Chlorohexadecane
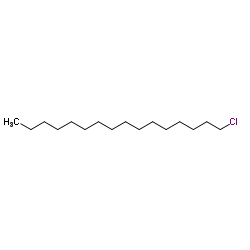
1-Chlorohexadecane structure
|
Common Name | 1-Chlorohexadecane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4860-03-1 | Molecular Weight | 260.886 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 321.8±5.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H33Cl | Melting Point | 8-14 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 138.1±3.4 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Haloalkane degradation and assimilation by Rhodococcus rhodochrous NCIMB 13064.
Microbiology 140 ( Pt 6) , 1433-42, (1994) The bacterium Rhodococcus rhodochrous NCIMB 13064, isolated from an industrial site, could use a wide range of 1-haloalkanes as sole carbon source but apparently utilized several different mechanisms simultaneously for assimilation of substrate. Catabolism of... |
|
|
Regiospecific internal desaturation of aliphatic compounds by a mutant Rhodococcus strain.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65(12) , 5636-8, (1999) A mutant Rhodococcus strain lacking the ability to utilize 1-chlorohexadecane was found to cis-desaturate aliphatic compounds, such as 1-chlorohexadecane, n-hexadecane, and heptadecanonitrile, yielding corresponding products with a double bond mainly at the n... |
|
|
Chlorinated fatty acid distribution in Mycobacterium convolutum phospholipids after growth on 1-chlorohexadecane.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53(1) , 10-3, (1987) The composition of phospholipids from Mycobacterium convolutum R22 was determined after growth at two temperatures (20 and 30 degrees C) with 1-chlorohexadecane as the substrate. Comparisons were made with the phospholipids of cells grown on n-hexadecane. Pho... |
|
|
Incorporation of chlorinated alkanes into fatty acids of hydrocarbon-utilizing mycobacteria.
J. Bacteriol. 156(3) , 1158-64, (1983) The cellular fatty acid composition of Mycobacterium vaccae JOB5 and Mycobacterium convolutum R22 was examined after growth on n-alkanes and compared with the fatty acids of the organisms after growth on 1-chlorohexadecane and 1-chlorooctadecane. Growth on n-... |
|
|
Characterization of the phase behaviour of a novel polymerizable lyotropic ionic liquid crystal.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17 , 23059-68, (2015) The development of new polymerizable lyotropic liquid crystals (LLCs) utilizing charged amphiphilic molecules such as those based on long chain imidazolium compounds, is a relatively new design direction for producing robust membranes with controllable nano-s... |
|
|
Electron impact mass spectrometry of alkanes in supersonic molecular beams.
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 6(2) , 120-31, (1995) The electron impact mass spectrometry of straight chain alkanes C8H18-C40H82, squalane, methylstearate, 1-chlorohexadecane, 1-bromohexadecane, and dioctylphthalate was studied by sampling them with supersonic molecular beams. A fly-through Brink-type electron... |