carbazeran
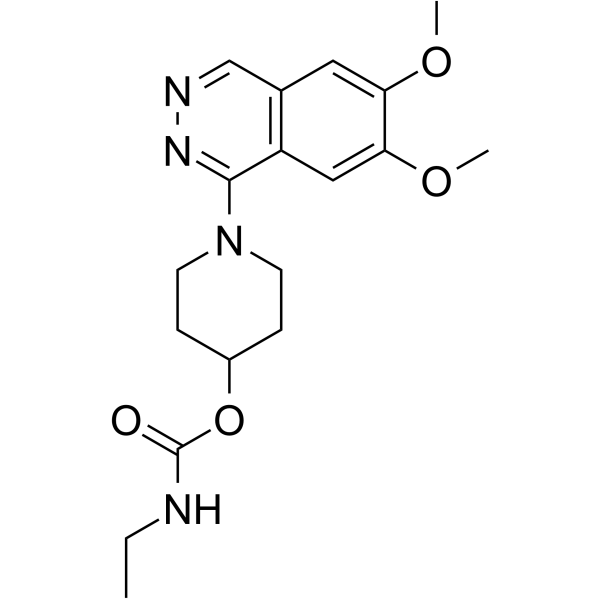
carbazeran structure
|
Common Name | carbazeran | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 70724-25-3 | Molecular Weight | 360.408 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 595.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H24N4O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 314.0±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Aldehyde oxidase activity in fresh human skin.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 42(12) , 2049-57, (2014) Human aldehyde oxidase (AO) is a molybdoflavoenzyme that commonly oxidizes azaheterocycles in therapeutic drugs. Although high metabolic clearance by AO resulted in several drug failures, existing in vitro-in vivo correlations are often poor and the extrahepa... |
|
|
A novel reaction mediated by human aldehyde oxidase: amide hydrolysis of GDC-0834.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 43 , 908-15, (2015) GDC-0834, a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor investigated as a potential treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, was previously reported to be extensively metabolized by amide hydrolysis such that no measurable levels of this compound were detected in human circ... |
|
|
Chronotropic and inotropic actions of amrinone, carbazeran and isobutylmethyl xanthine: role of phosphodiesterase inhibition.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 98 , 291-301, (1999) 1. The chronotropic and inotropic effects of amrinone, carbazeran and 3-isobutyl-1-methyl xanthine (IBMX) were examined in isolated preparations of papillary muscle and right atria from rabbit heart. The effects of the drugs on cardiac phosphodiesterase and c... |
|
|
Application of a Micropatterned Cocultured Hepatocyte System To Predict Preclinical and Human-Specific Drug Metabolism.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 44 , 172-9, (2016) Laboratory animal models are the industry standard for preclinical risk assessment of drug candidates. Thus, it is important that these species possess profiles of drug metabolites that are similar to those anticipated in human, since metabolites also could b... |
|
|
Deuterium isotope effects on drug pharmacokinetics. I. System-dependent effects of specific deuteration with aldehyde oxidase cleared drugs.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 40(3) , 625-34, (2012) The pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be altered by kinetic deuterium isotope effects. With specifically deuterated model substrates and drugs metabolized by aldehyde oxidase, we demonstrate how knowledge of the enzyme's reaction mechanism, species diff... |
|
|
The new inotropic phosphodiesterase inhibitors.
Arch. Int. Physiol. Biochim. 92(4) , S69-79, (1984) Compounds with phosphodiesterase inhibitory activity stimulate myocardial contractility by increasing the intracellular cyclic AMP concentrations. They can also increase Ca2+ entry and inhibit Ca2+ sequestration by the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Xanthines produc... |
|
|
Proteolysis of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase-II attenuates its ability to be inhibited by compounds which exert positive inotropic actions in cardiac tissue.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 36(23) , 4047-54, (1987) Extraction of frozen canine cardiac muscle rendered soluble over 90% of the cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase activity. The residual activity was membrane-bound. Ion exchange chromatography of the soluble activity on DE-52 allowed for the resolution of three disti... |
|
|
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: haemodynamic effects related to the treatment of cardiac failure.
Eur. Heart J. 3 Suppl D , 97-101, (1982)
|
|
|
Oxidative metabolism of carbazeran in vitro by liver cytosol of baboon and man.
Xenobiotica 15(3) , 237-42, (1985) The metabolism of carbazeran has been investigated in vitro using liver cytosol from dog, baboon and man. Carbazeran was not metabolized in cytosol prepared from dog liver but was rapidly metabolized to a single product in baboon- and human-liver cytosol. The... |
|
|
A species difference in the presystemic metabolism of carbazeran in dog and man.
Xenobiotica 14(12) , 935-45, (1984) The bioavailability of carbazeran and the metabolism of carbon-14 labelled drug have been studied in the dog and man following oral administration. The drug was moderately well absorbed in both species, but there was a marked difference in bioavailability and... |