camp sodium salt
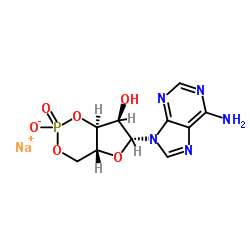
camp sodium salt structure
|
Common Name | camp sodium salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 37839-81-9 | Molecular Weight | 351.19 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 701.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H11N5NaO6P | Melting Point | 219 - 220ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 378ºC | |
|
H4 histamine receptors inhibit steroidogenesis and proliferation in Leydig cells.
J. Endocrinol. 223(3) , 241-53, (2014) The histamine H4 receptor (HRH4), discovered only 13 years ago, is considered a promising drug target for allergy, inflammation, autoimmune disorders and cancer, as reflected by a steadily growing number of scientific publications and patent applications. Alt... |
|
|
HBCDD-induced sustained reduction in mitochondrial membrane potential, ATP and steroidogenesis in peripubertal rat Leydig cells.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 282(1) , 20-9, (2015) Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDD), a brominated flame retardant added to various consumer products, is a ubiquitous environmental contaminant. We have previously shown that 6-hour exposure to HBCDD disturbs basal and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)-induced st... |
|
|
Activation of cAMP signaling attenuates impaired hepatic glucose disposal in aged male p21-activated protein kinase-1 knockout mice.
Endocrinology 155(6) , 2122-32, (2014) p21-activated protein kinase-1 (Pak1) plays a role in insulin secretion and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) production. Pak1(-/-) mice were found to carry a defect in ip pyruvate tolerance test (IPPTT), leading us to speculate whether Pak1 represses hepatic g... |
|
|
A novel mechanism for cyclic adenosine monophosphate-mediated memory formation: Role of amyloid beta.
Ann. Neurol. 75(4) , 602-7, (2014) Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) regulates long-term potentiation (LTP) and ameliorates memory in healthy and diseased brain. Increasing evidence shows that, under physiological conditions, low concentrations of amyloid β (Aβ) are necessary for LTP expre... |
|
|
Alpha-synuclein interferes with cAMP/PKA-dependent upregulation of dopamine β-hydroxylase and is associated with abnormal adaptive responses to immobilization stress.
Exp. Neurol. 252 , 63-74, (2014) Parkinson's disease (PD) is clinically characterized not only by motor symptoms but also by non-motor symptoms, such as anxiety and mood changes. Based on our previous study showing that overexpression of wild-type or mutant α-synuclein (α-SYN) interferes wit... |
|
|
PI3K/AKT and Mdm2 activation are associated with inhibitory effect of cAMP increasing agents on DNA damage-induced cell death in human pre-B NALM-6 cells.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 566 , 58-66, (2015) DNA damage response (DDR) consists of both proapoptotic and prosurvival signaling branches. Superiority of each signaling branch determines the outcome of DNA damage: death or allowing the repair. The present authors have previously shown that an increased in... |
|
|
A zebrafish embryo culture system defines factors that promote vertebrate myogenesis across species.
Cell 155(4) , 909-21, (2013) Ex vivo expansion of satellite cells and directed differentiation of pluripotent cells to mature skeletal muscle have proved difficult challenges for regenerative biology. Using a zebrafish embryo culture system with reporters of early and late skeletal muscl... |
|
|
Melatonin receptors trigger cAMP production and inhibit chloride movements in nonpigmented ciliary epithelial cells.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 352(1) , 119-28, (2015) Melatonin and its analog 5-MCA-NAT (5-methylcarboxyamino-N-acetyl tryptamine) are active compounds reducing intraocular pressure (IOP). This action is mediated through MT2 and the putative MT3 melatonin receptor, producing a transient reduction of IOP that la... |
|
|
Cyclic AMP-mediated suppression of neutrophil extracellular trap formation and apoptosis by the Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin.
Infect. Immun. 82(12) , 5256-69, (2014) The adenylate cyclase toxin (ACT) of Bordetella pertussis intoxicates target cells by generating supraphysiologic levels of intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP). Since ACT kills macrophages rapidly and potently, we asked whether ACT would also kill neutrophils. In... |
|
|
Intramitochondrial adenylyl cyclase controls the turnover of nuclear-encoded subunits and activity of mammalian complex I of the respiratory chain.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1853(1) , 183-91, (2015) In mammalian cells the nuclear-encoded subunits of complex I are imported into mitochondria, where they are assembled with mt-DNA encoded subunits in the complex, or exchanged with pre-existing copies in the complex. The present work shows that in fibroblast ... |