Psoralen
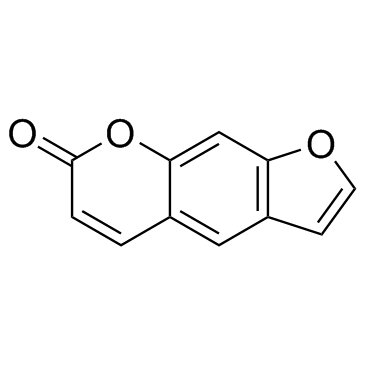
Psoralen structure
|
Common Name | Psoralen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 66-97-7 | Molecular Weight | 186.163 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 362.6±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H6O3 | Melting Point | 160-162 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 173.1±23.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Rotavirus increases levels of lipidated LC3 supporting accumulation of infectious progeny virus without inducing autophagosome formation.
PLoS ONE 9(4) , e95197, (2014) Replication of many RNA viruses benefits from subversion of the autophagic pathway through many different mechanisms. Rotavirus, the main etiologic agent of pediatric gastroenteritis worldwide, has been recently described to induce accumulation of autophagoso... |
|
|
Inhibition of human aldehyde oxidase activity by diet-derived constituents: structural influence, enzyme-ligand interactions, and clinical relevance.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 43(1) , 34-41, (2014) The mechanistic understanding of interactions between diet-derived substances and conventional medications in humans is nascent. Most investigations have examined cytochrome P450-mediated interactions. Interactions mediated by other phase I enzymes are unders... |
|
|
Assessment of a candidate marker constituent predictive of a dietary substance-drug interaction: case study with grapefruit juice and CYP3A4 drug substrates.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 351(3) , 576-84, (2014) Dietary substances, including herbal products and citrus juices, can perpetrate interactions with conventional medications. Regulatory guidances for dietary substance-drug interaction assessment are lacking. This deficiency is due in part to challenges unique... |
|
|
Inefficient Codon Usage Impairs mRNA Accumulation: the Case of the v-FLIP Gene of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus.
J. Virol. 89 , 7097-107, (2015) Latent Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) genomes encode a homolog of cellular FLICE-inhibitory proteins (termed v-FLIP) that activates NF-κB and can trigger important proinflammatory and antiapoptotic changes in latently infected cells. The prote... |
|
|
Rad51-mediated replication fork reversal is a global response to genotoxic treatments in human cells.
J. Cell Biol. 208(5) , 563-79, (2015) Replication fork reversal protects forks from breakage after poisoning of Topoisomerase 1. We here investigated fork progression and chromosomal breakage in human cells in response to a panel of sublethal genotoxic treatments, using other topoisomerase poison... |
|
|
Sequence of pathogenic events in cynomolgus macaques infected with aerosolized monkeypox virus.
J. Virol. 89(8) , 4335-44, (2015) To evaluate new vaccines when human efficacy studies are not possible, the FDA's "Animal Rule" requires well-characterized models of infection. Thus, in the present study, the early pathogenic events of monkeypox infection in nonhuman primates, a surrogate fo... |
|
|
RNF4-mediated polyubiquitination regulates the Fanconi anemia/BRCA pathway.
J. Clin. Invest. 125(4) , 1523-32, (2015) The Fanconi anemia/BRCA (FA/BRCA) pathway is a DNA repair pathway that is required for excision of DNA interstrand cross-links. The 17 known FA proteins, along with several FA-associated proteins (FAAPs), cooperate in this pathway to detect, unhook, and excis... |
|
|
Psoralen reverses docetaxel-induced multidrug resistance in A549/D16 human lung cancer cells lines.
Phytomedicine 21(7) , 970-7, (2014) Chemotherapy is the recommended treatment for advanced-stage cancers. However, the emergence of multidrug resistance (MDR), the ability of cancer cells to become simultaneously resistant to different drugs, limits the efficacy of chemotherapy. Previous studie... |
|
|
Cytochrome p450 enzymes mechanism based inhibitors: common sub-structures and reactivity.
Curr. Drug Metab. 6 , 413-54, (2005) The inhibition of human cytochrome P450s (CYPs) is one of the most common mechanisms which can lead to drug-drug interactions. The inhibition of CYPs can be reversible (competitive or non-competitive) or irreversible. Irreversible inhibition usually derives f... |
|
|
Prolonged antigen presentation following an acute virus infection requires direct and then cross-presentation.
J. Immunol. 193(8) , 4169-77, (2014) Antiviral CD8(+) T cell recognition of MHC class I-peptide complexes on the surface of professional APCs is a requisite step in an effective immune response following many potentially lethal infections. Although MHC class I-peptide production is thought to be... |