Methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate
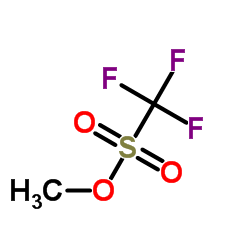
Methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate structure
|
Common Name | Methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 333-27-7 | Molecular Weight | 164.104 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 96.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H3F3O3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 38.3±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Synthesis of poly(meth)acrylates with thioether and tertiary sulfonium groups by ARGET ATRP and their use as siRNA delivery agents.
Biomacromolecules 16(1) , 236-45, (2015) The field of RNA interference depends on the development of safe and efficient carriers for short interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) delivery. Conventional cationic monomers for siRNA delivery have utilized the nitrogen heteroatom to produce cationic charge... |
|
|
Anaerobic Chemolithotrophic Growth of the Haloalkaliphilic Bacterium Strain MLMS-1 by Disproportionation of Monothioarsenate.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 49 , 6554-63, (2015) A novel chemolithotrophic metabolism based on a mixed arsenic-sulfur species has been discovered for the anaerobic deltaproteobacterium, strain MLMS-1, a haloalkaliphile isolated from Mono Lake, California, U.S. Strain MLMS-1 is the first reported obligate ar... |
|
|
Characterization of (18)F-dipicolylamine (DPA) derivatives in cells infected with influenza virus.
Nucl. Med. Biol. 42(3) , 283-91, (2015) Bis(Zn-dipicolylamine (Zn-DPA)) coordination complexes represent a new class of synthetic small molecules that can target anionic phosphatidylserine (PS) in the apoptotic cells with high affinity and specificity. In this study, we labeled Zn-DPA and Cy7-Zn-DP... |
|
|
Pyrobaculum yellowstonensis Strain WP30 Respires on Elemental Sulfur and/or Arsenate in Circumneutral Sulfidic Geothermal Sediments of Yellowstone National Park.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81 , 5907-16, (2015) Thermoproteales (phylum Crenarchaeota) populations are abundant in high-temperature (>70°C) environments of Yellowstone National Park (YNP) and are important in mediating the biogeochemical cycles of sulfur, arsenic, and carbon. The objectives of this study w... |
|
|
A standardized method for the construction of tracer specific PET and SPECT rat brain templates: validation and implementation of a toolbox.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0122363, (2015) High-resolution anatomical image data in preclinical brain PET and SPECT studies is often not available, and inter-modality spatial normalization to an MRI brain template is frequently performed. However, this procedure can be challenging for tracers where su... |
|
|
[Three cases of occupational methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate poisoning].
Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 28(4) , 304, (2010)
|
|
|
C-H activation on a diphosphine and hydrido-bridged diiridium complex: generation and detection of an active IrII-IrII species [(Cp*Ir)2(micro-dmpm)(micro-H)]+.
Dalton Trans. (27) , 3546-52, (2008) Reaction of [Cp*Ir(micro-H)](2) (5) (Cp* = eta(5)-C(5)Me(5)) with bis(dimethylphosphino)methane (dmpm) gives a new neutral diiridium complex [(Cp*Ir)(2)(micro-dmpm)(micro-H)(2)] (3). Treatment of 3 with methyl triflate at -30 degrees C results in the formatio... |
|
|
Identification and evaluation of [11C]GSK931145 as a novel ligand for imaging the type 1 glycine transporter with positron emission tomography.
Synapse 64(7) , 542-9, (2010) The type-1 glycine transporter (GlyT1) is an important target for the development of new medications for schizophrenia. A specific and selective positron emission tomography (PET) GlyT1 ligand would facilitate drug development studies to determine whether a d... |
|
|
A simple synthesis of [11C]methyl triflate.
Int. J. Rad. Appl. Instrum. A. 43(11) , 1383-5, (1992) [11C]Methyl triflate ([11C]methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate) was formed in high yield when [11C]methyl iodide in a nitrogen carrier was passed at 200 degrees C through a column containing graphitized carbon impregnated with 50% by weight of silver triflate. |
|
|
Convenient gas phase bromination of [11C]methane and production of [11C]methyl triflate.
Nucl. Med. Biol. 26(4) , 467-71, (1999)
|