Fleroxacin
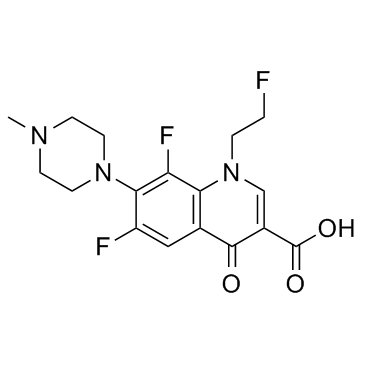
Fleroxacin structure
|
Common Name | Fleroxacin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 79660-72-3 | Molecular Weight | 369.338 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 535.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H18F3N3O3 | Melting Point | 264-266°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 277.6±30.1 °C | |
|
Computational modeling of novel inhibitors targeting the Akt pleckstrin homology domain.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 6983-92, (2009) Computational modeling continues to play an important role in novel therapeutics discovery and development. In this study, we have investigated the use of in silico approaches to develop inhibitors of the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of AKT (protein kinase... |
|
|
QSAR-based permeability model for drug-like compounds.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 2615-24, (2011) A QSAR model was developed for predicting intestinal drug permeability, one of the most important parameters when evaluating compounds in drug discovery projects. First, a set of relevant properties for establishing a drug-like chemical space was applied to a... |
|
|
Trend analysis of a database of intravenous pharmacokinetic parameters in humans for 670 drug compounds.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 36 , 1385-405, (2008) We present herein a compilation and trend analysis of human i.v. pharmacokinetic data on 670 drugs representing, to our knowledge, the largest publicly available set of human clinical pharmacokinetic data. This data set provides the drug metabolism scientist ... |
|
|
Physicochemical determinants of human renal clearance.
J. Med. Chem. 52 , 4844-52, (2009) Kidney plays an important role in the elimination of drugs, especially with low or negligible hepatic clearance. An analysis of the interrelation of physicochemical properties and the human renal clearance for a data set of 391 drugs or compounds tested in hu... |
|
|
Physicochemical space for optimum oral bioavailability: contribution of human intestinal absorption and first-pass elimination.
J. Med. Chem. 53 , 1098-108, (2010) Oral bioavailability (F) is a product of fraction absorbed (Fa), fraction escaping gut-wall elimination (Fg), and fraction escaping hepatic elimination (Fh). In this study, using a database comprised of Fa, Fg, Fh, and F values for 309 drugs in humans, an ana... |
|
|
Comparative evaluation of oral systemic exposure of 56 xenobiotics in rat, dog, monkey and human.
Xenobiotica 35 , 191-210, (2005) The prediction of human pharmacokinetics is often based on in vivo preclinical pharmacokinetic data. However, to date, no clear guidance has been available about the relative ability of the major preclinical species to estimate human oral exposure. The study ... |
|
|
Extrapolation of human pharmacokinetic parameters from rat, dog, and monkey data: Molecular properties associated with extrapolative success or failure.
J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 94 , 1467-83, (2005) Human pharmacokinetic parameters are often predicted prior to clinical study from in vivo preclinical pharmacokinetic data. Recent data suggest that extrapolation of monkey pharmacokinetic data tends to be the most accurate method for predicting human clearan... |
|
|
Quantitative comparison of the convulsive activity of combinations of twelve fluoroquinolones with five nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents.
Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 24(2) , 167-74, (2009) Concomitant administration of certain fluoroquinolone antimicrobials and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents (NSAIDs) induces serious convulsion in humans. There are differences in convulsive activity among fluoroquinolones and in the potentiation of fluoroq... |
|
|
Inter- and intramolecular photochemical reactions of fleroxacin.
Org. Lett. 11(9) , 1875-8, (2009) In the cation formed by photoinduced C-F bond cleavage in fleroxacin, intramolecular reaction with the N-ethyl chain is prevented by the electron-withdrawing effect of fluorine and intermolecular attack by nucleophiles is facilitated. |
|
|
Fleroxacin. A review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in various infections.
Drugs 49(5) , 794-850, (1995) The fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent fleroxacin has a broad spectrum of in vitro activity which encompasses most Gram-negative species (particularly Enterobacteriaceae) and a number of Gram-positive organisms, including methicillin-sensitive staphylococci.... |