5-Methylindole
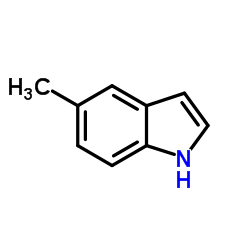
5-Methylindole structure
|
Common Name | 5-Methylindole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 614-96-0 | Molecular Weight | 131.17 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 269.0±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H9N | Melting Point | 60-62 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 114.7±11.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
NMR studies of the mode of binding of corepressors and inducers to Escherichia coli trp repressor.
Eur. J. Biochem. 235(3) , 804-13, (1996) The binding of the corepressors tryptophan and 5-methyltryptophan and of the inducers 3-indolepropionate, 3-indoleacrylate and 5-methylindole to the Escherichia coli trp repressor have been studied by 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Identification of the resonances of t... |
|
|
Generation of new protein kinase inhibitors utilizing cytochrome p450 mutant enzymes for indigoid synthesis.
J. Med. Chem. 47(12) , 3236-41, (2004) Indigoids, a class of bis-indoles, represent a promising protein kinase inhibitor scaffold. Oxidation of indole by cytochrome P450 (P450) has been shown to generate species (indoxyl, isatin) that couple to yield indigo and indirubin. Escherichia coli-expresse... |
|
|
Mass analyzed threshold ionization spectroscopy of 5-methylindole and 3-methylindole cations and the methyl substitution effect.
J. Chem. Phys. 120(11) , 5057-63, (2004) The vibrationally resolved mass analyzed threshold ionization spectra of jetcooled 5-methylindole (5MI) and 3-methylindole (3MI) have been recorded by ionizing via various vibronic levels of each species. The adiabatic ionization energies (IEs) of 5MI and 3MI... |
|
|
Tryptophan 7-halogenase (PrnA) structure suggests a mechanism for regioselective chlorination.
Science 309(5744) , 2216-9, (2005) Chlorinated natural products include vancomycin and cryptophycin A. Their biosynthesis involves regioselective chlorination by flavin-dependent halogenases. We report the structural characterization of tryptophan 7-halogenase (PrnA), which regioselectively ch... |
|
|
Structural features of L-tryptophan required for activation of TRAP, the trp RNA-binding attenuation protein of Bacillus subtilis.
J. Biol. Chem. 270(21) , 12452-6, (1995) A filter binding assay was used to determine the structural features of L-tryptophan required for activation of TRAP, the trp RNA-binding attenuation protein of Bacillus subtilis. We examined the ability of L-tryptophan and 26 of its analogs to activate TRAP.... |