pyrimethamine
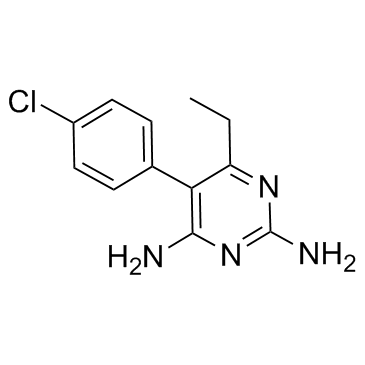
pyrimethamine structure
|
Common Name | pyrimethamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 58-14-0 | Molecular Weight | 248.711 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 368.4±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H13ClN4 | Melting Point | 233-234°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 176.6±30.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Multiresidue method for the determination of pharmacologically active substances in egg and honey using a continuous solid-phase extraction system and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
Food Chem. 178 , 63-9, (2015) A sensitive, selective, efficient gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of 22 pharmacologically active substances (antibacterials, nonsteroidal antiinflammatories, antiseptics, antiepileptics, lipid regulators, β-block... |
|
|
Host erythrocyte environment influences the localization of exported protein 2, an essential component of the Plasmodium translocon.
Eukaryotic Cell 14(4) , 371-84, (2015) Malaria parasites replicating inside red blood cells (RBCs) export a large subset of proteins into the erythrocyte cytoplasm to facilitate parasite growth and survival. PTEX, the parasite-encoded translocon, mediates protein transport across the parasitophoro... |
|
|
Disruption of IL-21 signaling affects T cell-B cell interactions and abrogates protective humoral immunity to malaria.
PLoS Pathog. 11(3) , e1004715, (2015) Interleukin-21 signaling is important for germinal center B-cell responses, isotype switching and generation of memory B cells. However, a role for IL-21 in antibody-mediated protection against pathogens has not been demonstrated. Here we show that IL-21 is p... |
|
|
N-terminal processing of proteins exported by malaria parasites.
Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 160(2) , 107-115, (2008) Malaria parasites utilize a short N-terminal amino acid motif termed the Plasmodium export element (PEXEL) to export an array of proteins to the host erythrocyte during blood stage infection. Using immunoaffinity chromatography and mass spectrometry, insight ... |
|
|
A chemical rescue screen identifies a Plasmodium falciparum apicoplast inhibitor targeting MEP isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59(1) , 356-64, (2014) The apicoplast is an essential plastid organelle found in Plasmodium parasites which contains several clinically validated antimalarial-drug targets. A chemical rescue screen identified MMV-08138 from the "Malaria Box" library of growth-inhibitory antimalaria... |
|
|
Pantothenic acid biosynthesis in the parasite Toxoplasma gondii: a target for chemotherapy.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(11) , 6345-53, (2014) Toxoplasma gondii is a major food pathogen and neglected parasitic infection that causes eye disease, birth defects, and fetal abortion and plays a role as an opportunistic infection in AIDS. In this study, we investigated pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) biosyn... |
|
|
Efficacy and safety of intermittent preventive treatment with sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine for malaria in African infants: a pooled analysis of six randomised, placebo-controlled trials.
Lancet 374(9700) , 1533-42, (2009) Intermittent preventive treatment (IPT) is a promising strategy for malaria control in infants. We undertook a pooled analysis of the safety and efficacy of IPT in infants (IPTi) with sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine in Africa.We pooled data from six double-blind, r... |
|
|
Effect of sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine resistance on the efficacy of intermittent preventive therapy for malaria control during pregnancy: a systematic review.
JAMA 297(23) , 2603-16, (2007) In malaria-endemic regions, strategies to control malaria during pregnancy rely on case management of malaria illness and anemia, and preventive measures such as insecticide-treated nets and intermittent preventive therapy (IPT).To determine the effect of inc... |
|
|
Pharmacokinetic profile of artemisinin derivatives and companion drugs used in artemisinin-based combination therapies for the treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children.
Clin. Pharmacokinet. 52(3) , 153-67, (2013) Malaria is one of the most common parasitic infections worldwide. Plasmodium falciparum is the most prevalent strain in Africa and also the most fatal. The disease especially affects children, with those under age 5 years accounting for approximately 86 % of ... |
|
|
The effect of antenatal monthly sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine, alone or with azithromycin, on foetal and neonatal growth faltering in Malawi: a randomised controlled trial.
Trop. Med. Int. Health 18(4) , 386-97, (2013) To examine the potential to reduce foetal and neonatal growth faltering through intermittent preventive treatment in pregnancy (IPTp) of malaria and reproductive tract infections with monthly sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine (SP), alone or with two doses of azithro... |