Ajmalicine
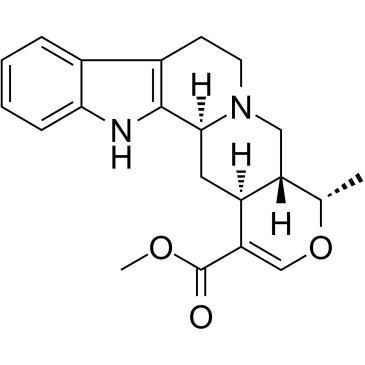
Ajmalicine structure
|
Common Name | Ajmalicine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 483-04-5 | Molecular Weight | 352.427 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 524.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H24N2O3 | Melting Point | 258°C (rough estimate) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 270.7±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Determination of terpenoid indole alkaloids in hairy roots of Rhazya stricta (Apocynaceae) by GC-MS.
Phytochem. Anal. 26 , 331-8, (2015) Rhazya stricta Decne. (Apocynaceae) is a medicinal plant rich in terpenoid indole alkaloids (TIAs), some of which possess important pharmacological properties. The study material including transgenic hairy root cultures have been developed and their potential... |
|
|
Synergistic and cytotoxic action of indole alkaloids produced from elicited cell cultures of Catharanthus roseus.
Pharm. Biol. 51(3) , 304-10, (2013) Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don (Apocynaceae) is a medicinal plant that produces more than 130 alkaloids, with special attention given to the production of the anti-hypertensive monomeric indole alkaloids, serpentine and ajmalicine, and the antitumor dimeric ... |
|
|
A differential response to chemical elicitors in Catharanthus roseus in vitro cultures.
Biotechnol. Lett. 31(4) , 591-5, (2009) The effects of methyl jasmonate, salicylic acid and ethylene on alkaloid accumulation in in vitro cell suspension, hairy roots and rootless shoot cultures of Catharanthus roseus were analyzed. Ajmalicine, but not catharanthine, accumulation was promoted by ja... |
|
|
Molecular modelling of human CYP2D6 and molecular docking of a series of ajmalicine- and quinidine-like inhibitors.
Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 42(4) , 362-71, (2008) 3D-models were created and refined for CYP2D6 and for its complexes with ajmalicine and quinidine. The influence of the conformation of the enzyme active site on its interaction with ligands was evaluated by performing three series of molecular docking on sel... |
|
|
Construction and expression of a dual vector for chemo-enzymatic synthesis of plant indole alkaloids in Escherichia coli.
Nat. Prod. Res. 24(8) , 759-66, (2010) A dual vector (pQE-70-STR1-SG) containing coding regions of strictosidine synthase (STR1, EC 4.3.3.2) and strictosidine glucosidase (SG, EC 3.2.1.105) from the Indian medicinal plant Rauvolfia serpentina was constructed. Functional expression of the vector in... |
|
|
Quantitative determination of reserpine, ajmaline, and ajmalicine in Rauvolfia serpentina by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. Sci. 44(9) , 557-60, (2006) A sensitive and reproducible reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method using photodiode array detection is established for the simultaneous quantitation of important root alkaloids of Rauvolfia serpentina, namely, reserpine, ajmaline... |
|
|
Brugada syndrome presenting as an acute coronary syndrome.
Acta Cardiol. 68(5) , 521-3, (2013) Syncope, non-specific ST-segment alterations and elevated troponin (cTn) are suspicious of an acute coronary syndrome (ACS). While an ACS is excluded when the coronary angiogram returns normal, the raised cTn should prompt a search for other potentially letha... |
|
|
In vitro propagation of Rauwolfia serpentina using liquid medium, assessment of genetic fidelity of micropropagated plants, and simultaneous quantitation of reserpine, ajmaline, and ajmalicine.
Methods Mol. Biol. 547 , 17-33, (2009) Rauwolfia serpentina holds an important position in the pharmaceutical world because of its immense anti-hypertensive properties resulting from the presence of reserpine in the oleoresin fraction of the roots. Poor seed viability, low seed germination rate, a... |
|
|
Water deficit stress effects on reactive oxygen metabolism in Catharanthus roseus; impacts on ajmalicine accumulation.
Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 62(1) , 105-11, (2008) In the present work, we have analysed the changes in the reactive oxygen metabolism of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. plants in terms of H(2)O(2) content, lipid peroxidation and the free radical quenching systems (non-enzymatic and enzymatic antioxidants) u... |
|
|
Antioxidant potentials and ajmalicine accumulation in Catharanthus roseus after treatment with giberellic acid.
Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 60(2) , 195-200, (2007) Changes in antioxidant potentials and indole alkaloid, ajmalicine, production were studied in Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. plants under treatment with gibberellic acid (GA(3)). The GA(3) treatments were given in two ways, foliar spray and soil drenching m... |