4,4′-methylenedianiline
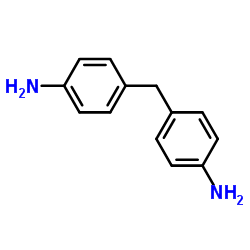
4,4′-methylenedianiline structure
|
Common Name | 4,4′-methylenedianiline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 101-77-9 | Molecular Weight | 198.264 | |
| Density | 1.15 | Boiling Point | 398-399 ºC (768 torr) | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H14N2 | Melting Point | 88-92 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 221 ºC | |
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Protective effect of Ferula gummosa hydroalcoholic extract against nitric oxide deficiency-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in rats renal tissues.
Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 37(2) , 136-41, (2015) Nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibition increases hypertension and causes renal injury. Ferula gummosa is used in Iranian traditional medicine for treatment of several diseases and has been reported to exert a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant action. Th... |
|
|
The efficacy and mechanism of apoptosis induction by hypericin-mediated sonodynamic therapy in THP-1 macrophages.
Int. J. Nanomedicine 10 , 821-38, (2015) To investigate the sonoactivity of hypericin (HY), together with its sonodynamic effect on THP-1 macrophages and the underlying mechanism.CCK-8 was used to examine cell viability. Confocal laser scanning microscopy was performed to assess the localization of ... |
|
|
Enhanced antioxidant capacity of dental pulp-derived iPSC-differentiated hepatocytes and liver regeneration by injectable HGF-releasing hydrogel in fulminant hepatic failure.
Cell. Transplant. 24(3) , 541-59, (2015) Acute hepatic failure (AHF) is a severe liver injury leading to sustained damage and complications. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) may be an alternative option for the treatment of AHF. In this study, we reprogrammed human dental pulp-derived fibrobla... |
|
|
Therapeutic Effects of Bupleurum Polysaccharides in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Mice.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0133212, (2015) Diabetes mellitus is related to low-grade chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. Bupleurum Polysaccharides (BPs), isolated from Bupleurum smithii var. parvifolium has anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative properties. However, little is known about its ther... |
|
|
The protective effects of tadalafil on renal damage following ischemia reperfusion injury in rats.
Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 31 , 454-62, (2015) Ischemia-reperfusion injury can cause renal damage, and phosphodiesterase inhibitors are reported to regulate antioxidant activity. We investigated the prevention of renal damage using tadalafil after renal ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury in rats. A total o... |
|
|
The short- and long-term effects of orally administered high-dose reduced graphene oxide nanosheets on mouse behaviors.
Biomaterials 68 , 100-13, (2015) Reduced graphene oxide (rGO), a carbon-based nanomaterial, has enormous potential in biomedical research, including in vivo cancer therapeutics. Concerns over the toxicity remain outstanding and must be investigated before clinical application. The effect of ... |
|
|
Biochemical and histopathological evidence on the beneficial effects of Tragopogon graminifolius in TNBS-induced colitis.
Pharm. Biol. 53(3) , 429-36, (2015) Tragopogon graminifolius DC. (Compositae) (TG) has been proposed as an efficacious remedy for gastrointestinal ulcers in Iranian traditional medicine.The present study evaluates the efficacy of TG on experimental colitis and the responsible mechanisms.After i... |
|
|
Chemical functionalization of graphene to augment stem cell osteogenesis and inhibit biofilm formation on polymer composites for orthopedic applications.
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(5) , 3237-52, (2015) Toward designing the next generation of resorbable biomaterials for orthopedic applications, we studied poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) composites containing graphene. The role, if any, of the functionalization of graphene on mechanical properties, stem cell respo... |
|
|
Inhibition of Hepatocyte Apoptosis: An Important Mechanism of Corn Peptides Attenuating Liver Injury Induced by Ethanol.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 , 22062-80, (2015) In this study, the effects of mixed corn peptides and synthetic pentapeptide (QLLPF) on hepatocyte apoptosis induced by ethanol were investigated in vivo. QLLPF, was previously characterized from corn protein hydrolysis, which had been shown to exert good fac... |
|
|
Hydrogen sulfide augments survival signals in warm ischemia and reperfusion of the mouse liver.
Surg. Today 45 , 892-903, (2015) Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) ameliorates hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury (IRI), but the precise mechanism remains elusive. We investigated whether sodium hydrogen sulfide (NaHS), a soluble derivative of H2S, would ameliorate hepatic IRI, and if so, via what... |