Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate
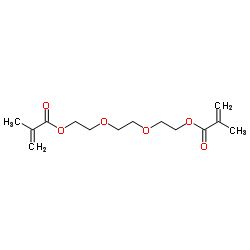
Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate structure
|
Common Name | Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 109-16-0 | Molecular Weight | 286.321 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 335.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H22O6 | Melting Point | -52°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 159.1±22.4 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Effect of methacrylated-based antibacterial monomer on orthodontic adhesive system properties.
Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 147(4 Suppl) , S82-7, (2015) Antibacterial adhesives were developed to reduce the incidence of white spot lesions in orthodontic patients. Compounds that contain triazine are known as effective antibacterial agents. The aims of this study were to develop an experimental orthodontic adhes... |
|
|
Interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel scaffolds for artificial cornea periphery.
J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 26(2) , 107, (2015) Three-dimensional scaffolds based on inverted colloidal crystals (ICCs) were fabricated from sequentially polymerized interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) hydrogels of poly(ethyleneglycol) and poly(acrylic acid). This high-strength, high-water-content IPN h... |
|
|
Bisphenol-A and residual monomer leaching from orthodontic adhesive resins and polycarbonate brackets: a systematic review.
Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 143(4 Suppl) , S104-12.e1-2, (2013) The objective of this systematic review was to assess the short- and long-term release of components of orthodontic adhesives and polycarbonate brackets in the oral environment.Electronic database searches of published and unpublished literature were performe... |
|
|
Bond Strength of Experimental Low-viscosity Resin Materials to Early Enamel Caries Lesions: Effect of Diluent/Solvent Addition.
J. Adhes. Dent. 17 , 117-23, (2015) To evaluate the effect of different concentrations of monomers and solvents/diluents on the microtensile bond strength (μTBS) bond strength of experimental low-viscosity resins (infiltrants) to enamel caries-like lesions (ECLL).Flat enamel blocks obtained fro... |
|
|
Microleakage of Class II restorations and microtensile bond strength to dentin of low-shrinkage composites.
Am. J. Dent. 26(5) , 271-7, (2013) To evaluate the microleakage of Class II cavities restored with experimental low-shrinking resin composites proposed for bulk filling and to measure their microtensile bond strength (microTBS) to dentin and compare to those of previously marketed low-shrinkag... |
|
|
Cariogenic bacteria degrade dental resin composites and adhesives.
J. Dent. Res. 92(11) , 989-94, (2013) A major reason for dental resin composite restoration replacement is related to secondary caries promoted by acid production from bacteria including Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans). We hypothesized that S. mutans has esterase activities that degrade dental r... |
|
|
Thio-urethanes improve properties of dual-cured composite cements.
J. Dent. Res. 93(12) , 1320-5, (2014) This study aims at modifying dual-cure composite cements by adding thio-urethane oligomers to improve mechanical properties, especially fracture toughness, and reduce polymerization stress. Thiol-functionalized oligomers were synthesized by combining 1,3-bis(... |
|
|
Bonding of simplified adhesive systems to caries-affected dentin of primary teeth.
J. Adhes. Dent. 15(5) , 439-45, (2013) To evaluate the bonding of simplified adhesive systems to sound and caries-affected dentin of primary teeth with microtensile (µTBS) and nanoleakage (NL) tests.Occlusal cavities were prepared in 36 sound second primary molars. Half of the specimens were submi... |
|
|
The effects of environment and cyclic fatigue on the mechanical properties of an indirect composite.
J. Dent. 40(10) , 787-92, (2012) The purpose of this study was to examine the flexure strength (σ) and fracture toughness (K(IC)) of three indirect dental composites (dentin, body, and incisal) with respect to loading (static and cyclic), testing environments (air and water) and ageing (0 (c... |
|
|
Remineralization of demineralized enamel via calcium phosphate nanocomposite.
J. Dent. Res. 91(10) , 979-84, (2012) Secondary caries remains the main problem limiting the longevity of composite restorations. The objective of this study was to investigate the remineralization of demineralized human enamel in vitro via a nanocomposite containing nanoparticles of amorphous ca... |