| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
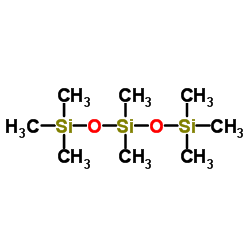 |
Octamethyltrisiloxane
CAS:107-51-7 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Hexamethyldisiloxane
CAS:107-46-0 |
|
 |
dichloroethane
CAS:107-06-2 |
|
 |
Water
CAS:7732-18-5 |
|
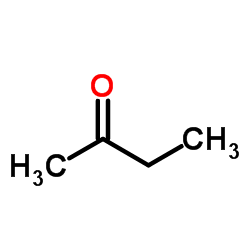 |
2-Butanone
CAS:78-93-3 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
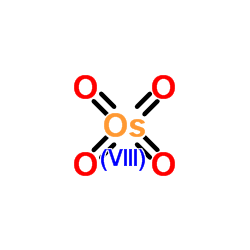 |
Osmium tetroxide
CAS:20816-12-0 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
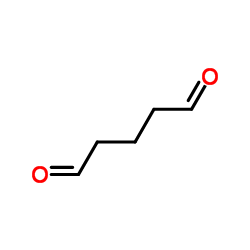 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |