CFTR(inh)-172
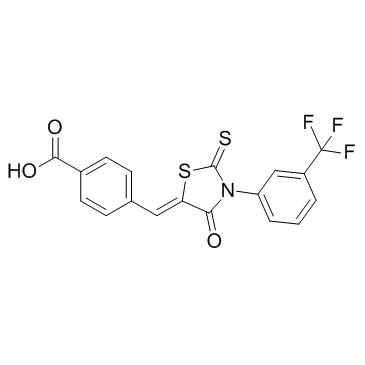
CFTR(inh)-172 structure
|
Common Name | CFTR(inh)-172 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 307510-92-5 | Molecular Weight | 409.402 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 555.7±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H10F3NO3S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 289.9±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced bleb-niche formation in epithelial cells is independent of actinomyosin contraction and enhanced by loss of cystic fibrosis transmembrane-conductance regulator osmoregulatory function.
MBio 6 , e02533, (2015) The opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa can infect almost any site in the body but most often targets epithelial cell-lined tissues such as the airways, skin, and the cornea of the eye. A common predisposing factor is cystic fibrosis (CF), caused by... |
|
|
Defective CFTR expression and function are detectable in blood monocytes: development of a new blood test for cystic fibrosis.
PLoS ONE 6 , e22212, (2011) Evaluation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) functional activity to assess new therapies and define diagnosis of cystic fibrosis (CF) is cumbersome. It is known that leukocytes express detectable levels of CFTR but the molecule has... |
|
|
Thiazolidinone CFTR inhibitor identified by high-throughput screening blocks cholera toxin-induced intestinal fluid secretion.
J. Clin. Invest. 110 , 1651-1658, (2002) Secretory diarrhea is the leading cause of infant death in developing countries and a major cause of morbidity in adults. The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein is required for fluid secretion in the intestine and airways and, ... |
|
|
In vivo pharmacology and antidiarrheal efficacy of a thiazolidinone CFTR inhibitor in rodents.
J. Pharm. Sci. 94 , 134-143, (2004) A small-molecule inhibitor of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), 3-[(3-trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5-[(4-carboxyphenyl)methylene]-2-thioxo-4-thiazolidinone (CFTR(inh)-172), reduces enterotoxin-induced intestinal fluid secretion in rod... |