CFTR(inh)-172
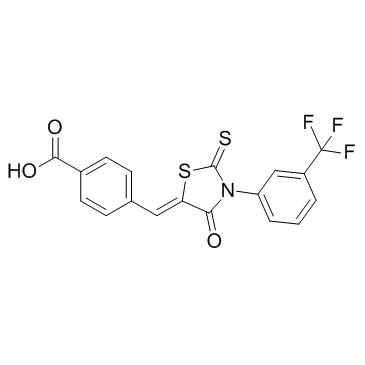
CFTR(inh)-172 structure
|
Common Name | CFTR(inh)-172 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 307510-92-5 | Molecular Weight | 409.402 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 555.7±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H10F3NO3S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 289.9±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of CFTR(inh)-172CFTR(inh)-172 is a potent and selective blocker of the CFTR chloride channel; reversibly inhibited CFTR short-circuit current in less than 2 minutes with a Ki of 300 nM. |
| Name | CFTRinh 172 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | CFTR(inh)-172 is a potent and selective blocker of the CFTR chloride channel; reversibly inhibited CFTR short-circuit current in less than 2 minutes with a Ki of 300 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 300 nM (CFTR)[1] |
| In Vitro | Inhibition by CFTR(inh)-172 is complete in approximately 10 minutes (t1/2=4 minutes) and is reversed after ishout with t1/2 approximately 5 minutes. CFTRinh-172 is nontoxic to FRT cells after 24 hours at concentrations up to 100 μM[1]. CFTR(inh)-172 does not alter CFTR unitary conductance (8 pS), but reduces open probability by > 90% with Ki=0.6 μM. This effect is due to increased mean channel closed time without changing mean channel open time. The Ki values for inhibition of Cl- current in wild-type, G551D, and G1349D CFTR are about 0.5 μM; however, Ki is significantly reduced to 0.2 μM for vF508 CFTR[2]. |
| In Vivo | A single intraperitoneal injection of CFTR(inh)-172 (250 μg/kg) in mice reduces by more than 90% cholera toxin–induced fluid secretion in the small intestine over 6 hours. CFTR(inh)-172 is nontoxic at high concentrations in mouse models. CFTRinh-172 significantly reduces fluid secretion to that in saline control loops, whereas an inactive CFTRinh-172 analog does not inhibit fluid secretion[1]. |
| Cell Assay | CFTR(inh)-172 is diluted in DMSO as a 10 mM stock solution and diluted with appropriate medium. Fischer rat thyroid (FRT) cells coexpressing human wild-type CFTR and the halide indicator YFP-H148Q are generated. Cell toxicity is assayed by the dihydrorhodamine method at 24 hours after cell incubation with 0–1,000 μM inhibitor CFTR(inh)-172[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: Animal toxicity is assessed by measurement of serum chemistries and hematology in mice at 5 days after daily intraperitoneal injections with 0-1,000 μg/kg CFTR(inh)-172[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 555.7±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H10F3NO3S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 409.402 |
| Flash Point | 289.9±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 409.005432 |
| PSA | 115.00000 |
| LogP | 4.51 |
| Appearance of Characters | yellow |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.698 |
| Storage condition | Store at +4°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: ≥10mg/mL |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H317-H319-H335-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P273-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi,N |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38-43-50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36/37-60-61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
|
~68% 
CFTR(inh)-172 CAS#:307510-92-5 |
| Literature: THE REGENTS OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Patent: US2011/105565 A1, 2011 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 28 ; |
|
~% 
CFTR(inh)-172 CAS#:307510-92-5 |
| Literature: US2011/105565 A1, ; |
|
~% 
CFTR(inh)-172 CAS#:307510-92-5 |
| Literature: US2011/105565 A1, ; |
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced bleb-niche formation in epithelial cells is independent of actinomyosin contraction and enhanced by loss of cystic fibrosis transmembrane-conductance regulator osmoregulatory function.
MBio 6 , e02533, (2015) The opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa can infect almost any site in the body but most often targets epithelial cell-lined tissues such as the airways, skin, and the cornea of the eye. A co... |
|
|
Defective CFTR expression and function are detectable in blood monocytes: development of a new blood test for cystic fibrosis.
PLoS ONE 6 , e22212, (2011) Evaluation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) functional activity to assess new therapies and define diagnosis of cystic fibrosis (CF) is cumbersome. It is known that leukoc... |
|
|
Thiazolidinone CFTR inhibitor identified by high-throughput screening blocks cholera toxin-induced intestinal fluid secretion.
J. Clin. Invest. 110 , 1651-1658, (2002) Secretory diarrhea is the leading cause of infant death in developing countries and a major cause of morbidity in adults. The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein is requ... |
| CFTR INHIBITOR-172 |
| Benzoic acid, 4-[(Z)-[4-oxo-2-thioxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5-thiazolidinylidene]methyl]- |
| CFTR(inh)-172 |
| 4-[(Z)-{4-Oxo-2-thioxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,3-thiazolidin-5-ylidene}methyl]benzoic acid |
| 4-[(E)-{4-Oxo-2-thioxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,3-thiazolidin-5-ylidene}methyl]benzoic acid |
| Benzoic acid, 4-[(E)-[4-oxo-2-thioxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5-thiazolidinylidene]methyl]- |
| 4-[[4-Oxo-2-thioxo-3-[3-trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5-thiazolidinylidene]methyl]benzoicacid |
| CFTRinh-172 |
![4-Thiazolidinone,2-thioxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/455/315-08-2.png)