Narciclasine
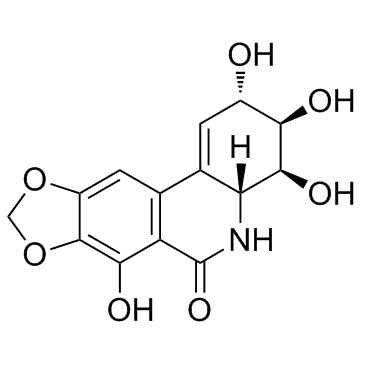
Narciclasine structure
|
Common Name | Narciclasine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 29477-83-6 | Molecular Weight | 307.255 | |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 733.8±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H13NO7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 397.6±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Simultaneous quantification of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids from Zephyranthes grandiflora by UPLC-DAD/ESI-MS/MS.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 71 , 187-92, (2012) A rapid, simple and sensitive ultra performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection method (UPLC-DAD) was developed and validated for quantification of four biologically important Amaryllidaceae alkaloids viz. lycoramine, hamayne, haemanthamine and to... |
|
|
Seasonal accumulation of major alkaloids in organs of pharmaceutical crop Narcissus Carlton.
Phytochemistry 88 , 43-53, (2013) Narcissus pseudonarcissus (L.) cv. Carlton is being cultivated as a main source of galanthamine from the bulbs. After galanthamine, haemanthamine and narciclasine are the next most abundant alkaloids in this cultivar. Both these compounds are promising chemic... |
|
|
[Study on chemical constituents of the bulbs of Lycoris longituba].
Zhong Yao Cai 34(9) , 1366-8, (2011) To study the chemical constituents of the Bulbs of Lycoris longituba.The chemical constituents were isolated and purified by means of chromatographic techniques and their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods.Six compounds were isolated and iden... |
|
|
Selective cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitory activity of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 3233-7, (2009) A library of natural and semi-synthetic Amaryllidaceae alkaloids was screened for cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitory activity. Of the crinane, lycorane and galanthamine representatives examined two semi-synthetic silylated lycorane analogues, accessed vi... |
|
|
Antineoplastic agents. 454. Synthesis of the strong cancer cell growth inhibitors trans-dihydronarciclasine and 7-deoxy-trans-dihydronarciclasine (1a).
J. Nat. Prod. 72(7) , 1279-82, (2009) To further pursue the antineoplastic leads offered by our isolation of trans-dihydronarciclasine (1a) and 7-deoxy-trans-dihydronarciclasine (1c) from two medicinal plant species of the Amaryllidaceae family, a practical palladium-catalyzed hydrogenation proce... |
|
|
Antineoplastic agents. 550. Synthesis of 10b(s)-epipancratistatin from (+)-narciclasine.
J. Nat. Prod. 70(3) , 417-22, (2007) By means of a five-step reaction sequence, narciclasine (2a), isolated from Narcissus sp., was converted to 10b(S)-epipancratistatin (3a) in 5.7% overall yield. The key step entailed a radical-initiated 10b,1 C-O cleavage employing tributyltin hydride to yiel... |
|
|
Antineoplastic agents 500. Narcistatin.
J. Nat. Prod. 66(1) , 92-6, (2003) An efficient procedure was found for synthetic conversion of the sparingly soluble anticancer isocarbostyril narciclasine (1), a component of various Narcissus species, to a cyclic phosphate designated narcistatin (3b). The reaction between narciclasine, tetr... |
|
|
Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunctions are early events in narciclasine-induced programmed cell death in tobacco Bright Yellow-2 cells.
Physiol. Plant. 144(1) , 48-58, (2012) Narciclasine (NCS) is a plant growth inhibitor isolated from the secreted mucilage of Narcissus tazetta bulbs. It is a commonly used anticancer agent in animal systems. In this study, we provide evidence to show that NCS also acts as an agent in inducing prog... |
|
|
Concentration-dependent effects of narciclasine on cell cycle progression in Arabidopsis root tips.
BMC Plant Biol. 11 , 184, (2011) Narciclasine (NCS) is an Amaryllidaceae alkaloid isolated from Narcissus tazetta bulbs. NCS has inhibitory effects on a broad range of biological activities and thus has various potential practical applications. Here we examine how NCS represses plant root gr... |
|
|
Narciclasine modulates polar auxin transport in Arabidopsis roots.
J. Plant Physiol. 168(11) , 1149-56, (2011) Plant development displays an exceptional plasticity and adaptability that involves the dynamic, asymmetric distribution of the phytohormone auxin. Polar auxin flow, which requires transport facilitators of the PIN family, largely contributes to the establish... |