Asoxime dichloride
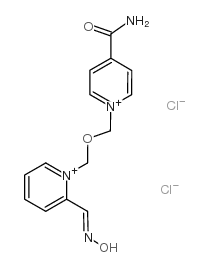
Asoxime dichloride structure
|
Common Name | Asoxime dichloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 34433-31-3 | Molecular Weight | 359.20800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H16Cl2N4O3 | Melting Point | 145-147ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Effect of reversible ligands on oxime-induced reactivation of sarin- and cyclosarin-inhibited human acetylcholinesterase.
Toxicol. Lett. 232(3) , 557-65, (2015) Poisoning by organophosphorus compounds (OP) used as pesticides and nerve agents is due to irreversible inhibition of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Oximes have been widely recognized for their potency to reactivate the inhibited enzyme. The limited ... |
|
|
The effect of oxime reactivators on muscarinic receptors: functional and binding examinations.
Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 31(3) , 364-70, (2011) The antidotal treatment of organophosphorus poisoning is still a problematic issue since no versatile antidote has been developed yet. In our study, we focused on an interesting property, which does not relate to the reactivation of inhibited acetylcholineste... |
|
|
Syntheses and in vitro evaluations of uncharged reactivators for human acetylcholinesterase inhibited by organophosphorus nerve agents.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 203(1) , 81-4, (2013) Organophosphorus nerve agents (OPNAs) are highly toxic compounds that represent a threat to both military and civilian populations. They cause an irreversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), by the formation of a covalent P-O bond with the catalyti... |
|
|
Investigation of oxidative stress in blood, brain, kidney, and liver after oxime antidote HI-6 application in a mouse experimental model.
Drug Chem. Toxicol. 34(3) , 255-60, (2011) Oxime reactivator HI-6 (asoxime, in some sources) is a potent antidote suitable for treatment of intoxication by nerve agents. Despite the fact that HI-6 is considered for practical application in emergency situations, the impact of HI-6 on patients' bodies h... |
|
|
Photostability of antidotal oxime HI-6, impact on drug development.
Drug Test. Anal. 4(3-4) , 208-14, (2012) HI-6 exhibits superior efficacy in the therapy of intoxication by different highly toxic organophosphorus nerve agents. Therefore HI-6 is a promising candidate for the development of new antidotes against nerve agents. For ethical and safety reasons antidotes... |
|
|
Hyaluronidase: its effects on HI-6 dichloride and dimethanesulphonate pharmacokinetic profile in pigs.
Toxicol. Lett. 220(2) , 167-71, (2013) Pigs were administered intramuscularly molar equivalents of HI-6 salts (HI-6 dichloride 10.71 mg/kg and HI-6 DMS 13.59 mg/kg) either with or without hyaluronidase (60 U/kg). Hyaluronidase is supposed to increase tissue permeability and diminishes discomfort c... |
|
|
Restoration of nerve agent inhibited muscle force production in human intercostal muscle strips with HI 6.
Toxicol. Lett. 206(1) , 72-6, (2011) An important factor for successful therapy of poisoning with organophosphorus compounds (OP) is the rapid restoration of blocked respiratory muscle function. To achieve this goal, oximes are administered for reactivation of inhibited acetylcholinesterase (ACh... |
|
|
A comparison of the potency of a novel bispyridinium oxime K203 and currently available oximes (obidoxime, HI-6) to counteract the acute neurotoxicity of sarin in rats.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 111(5) , 333-8, (2012) The neuroprotective effects of a newly developed oxime K203 and currently available oximes (obidoxime, HI-6) in combination with atropine in rats poisoned with sarin were studied. The sarin-induced neurotoxicity was monitored using a functional observatory ba... |
|
|
A comparison of the efficacy of newly developed reversible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase with commonly used pyridostigmine as pharmacological pre-treatment of soman-poisoned mice.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 110(4) , 322-6, (2012) The ability of three newly developed reversible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) (K298, K344 and K474) and currently available carbamate pyridostigmine to increase the resistance of mice against soman and the efficacy of antidotal treatment of soman-... |
|
|
A common mechanism for resistance to oxime reactivation of acetylcholinesterase inhibited by organophosphorus compounds.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 203(1) , 72-6, (2013) Administration of oxime therapy is currently the standard approach used to reverse the acute toxicity of organophosphorus (OP) compounds, which is usually attributed to OP inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Rate constants for reactivation of OP-inhibi... |