CTB
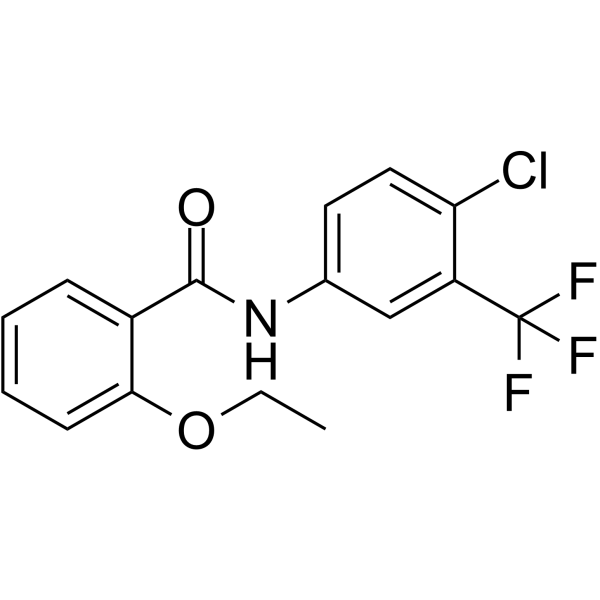
CTB structure
|
Common Name | CTB | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 451491-47-7 | Molecular Weight | 343.73 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H13ClF3NO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
A Bmp Reporter Transgene Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Model as a Tool to Identify and Characterize Chemical Teratogens.
Toxicol. Sci. 146 , 374-85, (2015) Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) were first isolated from mouse embryos more than 30 years ago. They have proven invaluable not only in generating genetically modified mice that allow for analysis of gene function in tissue development and homeostasis but also as ... |
|
|
Mechanism of scrapie prion precipitation with phosphotungstate anions.
ACS Chem. Biol. 10 , 1269-77, (2015) The phosphotungstate anion (PTA) is widely used to facilitate the precipitation of disease-causing prion protein (PrP(Sc)) from infected tissue for applications in structural studies and diagnostic approaches. However, the mechanism of this precipitation is n... |
|
|
Multiplexed detection of lectins using integrated glycan-coated microring resonators.
Biosens. Bioelectron. 80 , 682-90, (2016) We present the systematic design, fabrication, and characterization of a multiplexed label-free lab-on-a-chip biosensor using silicon nitride (SiN) microring resonators. Sensor design is addressed through a systematic approach that enables optimizing the sens... |
|
|
Developmental remodeling of relay cells in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in the absence of retinal input.
Neural Dev. 10 , 19, (2015) The dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN) of the mouse has been an important experimental model for understanding thalamic circuit development. The developmental remodeling of retinal projections has been the primary focus, however much less is known about... |
|
|
Modeling the effects of cyclodextrin on intracellular membrane vesicles from Cos-7 cells prepared by sonication and carbonate treatment.
PeerJ 3 , e1351, (2015) Cholesterol has important functions in the organization of membrane structure and this may be mediated via the formation of cholesterol-rich, liquid-ordered membrane microdomains often referred to as lipid rafts. Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (cyclodextrin) is com... |
|
|
Cortico-Cortical Connectivity Within Ferret Auditory Cortex.
J. Comp. Neurol. 523 , 2187-210, (2015) Despite numerous studies of auditory cortical processing in the ferret (Mustela putorius), very little is known about the connections between the different regions of the auditory cortex that have been characterized cytoarchitectonically and physiologically. ... |
|
|
Myelin basic protein induces neuron-specific toxicity by directly damaging the neuronal plasma membrane.
PLoS ONE 9(9) , e108646, (2014) The central nervous system (CNS) insults may cause massive demyelination and lead to the release of myelin-associated proteins including its major component myelin basic protein (MBP). MBP is reported to induce glial activation but its effect on neurons is st... |
|
|
Expression and functional validation of heat-labile enterotoxin B (LTB) and cholera toxin B (CTB) subunits in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa).
Springerplus 4 , 148, (2015) We expressed the heat-labile enterotoxin B (LTB) subunit from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and the cholera toxin B (CTB) subunit from Vibrio cholerae under the control of the rice (Oryza sativa) globulin (Glb) promoter. Binding of recombinant LTB and CTB ... |
|
|
A 3.7 kb fragment of the mouse Scn10a gene promoter directs neural crest but not placodal lineage EGFP expression in a transgenic animal.
J. Neurosci. 35 , 8021-34, (2015) Under physiological conditions, the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.8 is expressed almost exclusively in primary sensory neurons. The mechanism restricting Nav1.8 expression is not entirely clear, but we have previously described a 3.7 kb fragment of the Sc... |
|
|
A Conformational Shift in the Dissociated Cholera Toxin A1 Subunit Prevents Reassembly of the Cholera Holotoxin.
Toxins (Basel.) 7 , 2674-84, (2015) Cholera toxin (CT) consists of a catalytic A1 subunit, an A2 linker, and a homopentameric cell-binding B subunit. The intact holotoxin moves by vesicle carriers from the cell surface to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) where CTA1 is released from the rest of th... |