Sodium (2R,3R,4S,5S)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy-6-oxohexyl hydrogenphosphate
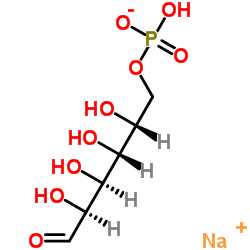
Sodium (2R,3R,4S,5S)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy-6-oxohexyl hydrogenphosphate structure
|
Common Name | Sodium (2R,3R,4S,5S)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy-6-oxohexyl hydrogenphosphate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 70442-25-0 | Molecular Weight | 282.118 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12NaO9P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Biomineralization in diatoms-phosphorylated saccharides are part of Stephanopyxis turris biosilica.
Carbohydr. Res. 365 , 52-60, (2013) Diatoms-unicellular algae with silicified cell walls-have become model organisms for investigations of biomineralization processes. Numerous studies suggest the importance of biosilica-associated or even embedded biomolecules for the biosilica formation. Such... |
|
|
The DMAP interaction domain of UDP-GlcNAc:lysosomal enzyme N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase is a substrate recognition module.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(25) , 10246-51, (2013) UDP-GlcNAc:lysosomal enzyme N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase (GlcNAc-1-phosphotransferase) is an α2β2γ2 heterohexamer that mediates the initial step in the formation of the mannose 6-phosphate recognition signal on lysosomal acid hydrolases. We previo... |
|
|
Mannose-6-phosphate regulates destruction of lipid-linked oligosaccharides.
Mol. Biol. Cell 22(17) , 2994-3009, (2011) Mannose-6-phosphate (M6P) is an essential precursor for mannosyl glycoconjugates, including lipid-linked oligosaccharides (LLO; glucose(3)mannose(9)GlcNAc(2)-P-P-dolichol) used for protein N-glycosylation. In permeabilized mammalian cells, M6P also causes spe... |
|
|
In vivo targeting of alveolar macrophages via RAFT-based glycopolymers.
Biomaterials , (2012) Targeting cell populations via endogenous carbohydrate receptors is an appealing approach for drug delivery. However, to be effective, this strategy requires the production of high affinity carbohydrate ligands capable of engaging with specific cell-surface l... |
|
|
Mannose 6 phosphorylation of lysosomal enzymes controls B cell functions.
J. Cell Biol. 208(2) , 171-80, (2015) Antigen processing and presentation and cytotoxic targeting depend on the activities of several lysosomal enzymes that require mannose 6-phosphate (M6P) sorting signals for efficient intracellular transport and localization. In this paper, we show that mice d... |
|
|
Mannose 6 dephosphorylation of lysosomal proteins mediated by acid phosphatases Acp2 and Acp5.
Mol. Cell. Biol. 32(4) , 774-82, (2012) Mannose 6-phosphate (Man6P) residues represent a recognition signal required for efficient receptor-dependent transport of soluble lysosomal proteins to lysosomes. Upon arrival, the proteins are rapidly dephosphorylated. We used mice deficient for the lysosom... |
|
|
Mannose 6-phosphate receptor homology (MRH) domain-containing lectins in the secretory pathway.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1810(9) , 815-26, (2011) The mannose 6-phosphate receptor homology (MRH) domain-containing family of proteins, which include recycling receptors (mannose 6-phosphate receptors, MPRs), resident endoplasmic reticulum (ER) proteins (glucosidase II β-subunit, XTP3-B, OS-9), and a Golgi g... |
|
|
A zebrafish model of PMM2-CDG reveals altered neurogenesis and a substrate-accumulation mechanism for N-linked glycosylation deficiency.
Mol. Biol. Cell 23(21) , 4175-87, (2012) Congenital disorder of glycosylation (PMM2-CDG) results from mutations in pmm2, which encodes the phosphomannomutase (Pmm) that converts mannose-6-phosphate (M6P) to mannose-1-phosphate (M1P). Patients have wide-spectrum clinical abnormalities associated with... |
|
|
Extensive mannose phosphorylation on leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) controls its extracellular levels by multiple mechanisms.
J. Biol. Chem. 286(28) , 24855-64, (2011) In addition to soluble acid hydrolases, many nonlysosomal proteins have been shown to bear mannose 6-phosphate (Man-6-P) residues. Quantification of the extent of mannose phosphorylation and the relevance to physiological function, however, remain poorly defi... |
|
|
Targeted TFO delivery to hepatic stellate cells.
J. Control. Release 155(2) , 326-30, (2011) Triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) represent an antigene approach for gene regulation through direct interaction with genomic DNA. While this strategy holds great promise owing to the fact that only two alleles need silencing to impact gene regulation, d... |