Crotonaldehyde
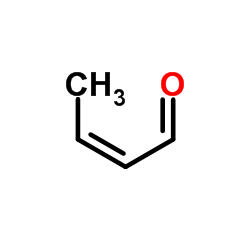
Crotonaldehyde structure
|
Common Name | Crotonaldehyde | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 123-73-9 | Molecular Weight | 70.090 | |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 104.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H6O | Melting Point | −76 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 4.6±4.3 °C | |
| Symbol |





GHS02, GHS05, GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Methyl vinyl ketone, a toxic ingredient in cigarette smoke extract, modifies glutathione in mouse melanoma cells.
Chem. Pharm. Bull. 62(8) , 772-8, (2014) Cigarette smoke contains many harmful chemicals, which contribute to the pathogenesis of smoking-related diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cancer and cardiovascular disease. The cytotoxicity of cigarette smoke is well documented, but the... |
|
|
Purity Determination of Acetaldehyde in an Acetaldehyde Certified Reference Material.
Anal. Sci. 31 , 463-8, (2015) Acetaldehyde is regulated as a toxic substance in various fields, and the method for monitoring or analysis of acetaldehyde is important. However, handling is difficult because of the high reactivity and low boiling point of acetaldehyde. Therefore, a referen... |
|
|
Cigarette smoke has sensory effects through nicotinic and TRPA1 but not TRPV1 receptors on the isolated mouse trachea and larynx.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 309 , L812-20, (2015) Cigarette smoke (CS) exposes chemosensory nerves in the airways to a multitude of chemicals, some acting through the irritant receptors TRPV1 and TRPA1 but potentially also through nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR). Our aim was to characterize the dif... |
|
|
Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 receptor activation in vitro and in vivo by pro-tussive agents: GRC 17536 as a promising anti-tussive therapeutic.
PLoS ONE 9(5) , e97005, (2014) Cough is a protective reflex action that helps clear the respiratory tract which is continuously exposed to airborne environmental irritants. However, chronic cough presents itself as a disease in its own right and despite its global occurrence; the molecular... |
|
|
Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) channel as emerging target for novel analgesics and anti-inflammatory agents.
J. Med. Chem. 53 , 5085-107, (2010)
|
|
|
Reactive Carbonyl Species Derived from Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 6293-6, (2015) Inflammation-related reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are associated with the development of cancer. ROS and RNS can directly damage biomacromolecules such as proteins, DNA, and lipids. Lipid peroxidation, however, can result ... |
|
|
Reduction of lipid peroxidation products and advanced glycation end-product precursors by cyanobacterial aldo-keto reductase AKR3G1—a founding member of the AKR3G subfamily.
FASEB J. 29(1) , 263-73, (2015) The purpose of this study was to investigate the origin and function of the aldo-keto reductase (AKR) superfamily as enzymes involved in the detoxification of xenobiotics. We used the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 as a model organism and sequence ... |
|
|
Crotonaldehyde induces apoptosis in alveolar macrophages through intracellular calcium, mitochondria and p53 signaling pathways.
J. Toxicol. Sci. 38(2) , 225-35, (2013) Crotonaldehyde, a highly electrophilic α, β-unsaturated aldehyde, is a ubiquitous environmental pollutant and a risk factor for multiple respiratory diseases. Crotonaldehyde is highly volatile and hydrophilic, so it is efficiently absorbed in the respiratory ... |
|
|
Crotonaldehyde induces heat shock protein 72 expression that mediates anti-apoptotic effects in human endothelial cells
Toxicol. Lett. 223(2) , 116-23, (2013) • Crotonaldehyde induces HSP72 up-regulation in HUVECs. • HSP72 induction is mediated by JNK-HSF1 pathway. • HSP72 expression by crotonaldehyde requires calcium ions and ROS. • Up-regulation of HSP72 protects against crotonaldehyde-induced apoptosis in HUVECs... |
|
|
Consideration of reactivity to acute fish toxicity of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl ketones and aldehydes.
SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 23(1-2) , 169-84, (2012) To understand the key factor for fish toxicity of 11 α,β-unsaturated carbonyl aldehydes and ketones, we used quantum chemical calculations to investigate their Michael reactions with methanethiol or glutathione. We used two reaction schemes, with and without ... |