magnesium aspartate dihydrate
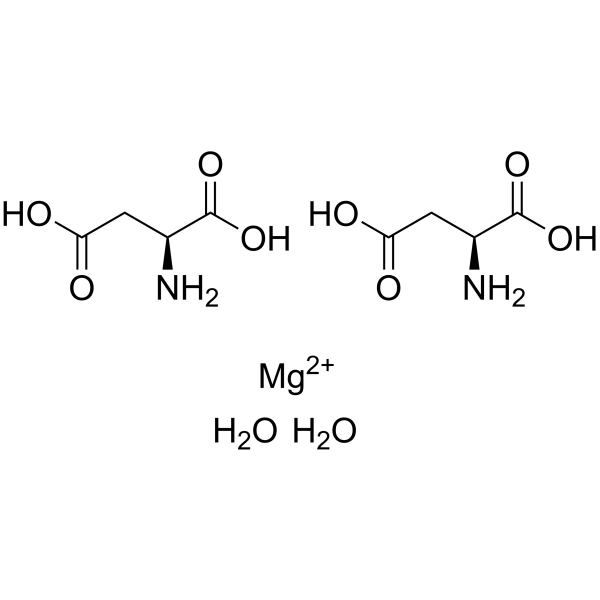
magnesium aspartate dihydrate structure
|
Common Name | magnesium aspartate dihydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 215533-00-9 | Molecular Weight | 324.525 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H16MgN2O10 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
The free radical scavenger, edaravone, ameliorates delayed neuropsychological sequelae after acute carbon monoxide poisoning in rabbits.
Undersea Hyperb. Med. 40(3) , 223-9, (2013) The mechanism underlying delayed neuropsychological sequelae (DNS) after acute carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning is unclear. There are no effective treatments for DNS. As part of a new generation of antioxidants, edaravone has been reported to improve clinical o... |
|
|
Evaluation of enantiomeric purity of magnesium-L-aspartate dihydrate.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 102 , 100-9, (2014) Magnesium supplementation in form of organic magnesium salts is a very popular practice. We examined the enantiomeric purity of "Magnesium aspartate dihydrate" monographed in the European Pharmacopeia. A chiral capillary zone electrophoresis using (2-hydroxyp... |
|
|
Effect of heavy metals and phenol on bacterial decolourisation and COD reduction of sucrose-aspartic acid Maillard product.
J. Environ. Sci. (China) 25(1) , 172-80, (2013) Melanodins are amino-carbonyl complex, predominantly present in sugarcane molasses based distillery wastewater as major source of colourant. The microbial decolourisation of melanoidin is a challenge due to its binding property with other co-pollutants of dis... |
|
|
[I/D angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism: structural changes in the myocardium and predictive value in chronic heart failure].
Lik. Sprava (8) , 36-42, (2012) The article presents data regarding links of I/D angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) gene polymorphism and structural changes in the myocardium and predictive value in chronic heart failure (CHF). We did not find association of I/D ACE gene polymorphism and s... |
|
|
Erythropoietin derived by chemical synthesis.
Science 342(6164) , 1357-60, (2013) Erythropoietin is a signaling glycoprotein that controls the fundamental process of erythropoiesis, orchestrating the production and maintenance of red blood cells. As administrated clinically, erythropoietin has a polypeptide backbone with complex dishomogen... |
|
|
Total synthesis of human galanin-like peptide through an aspartic acid ligation.
Org. Lett. 15(24) , 6128-31, (2013) Human galanin-like peptide (hGALP) is a newly discovered hypothalamic peptide that plays important roles in the regulation of food intake and energy balance. Here, we demonstrate that the aspartic acid ligation can be employed to achieve an efficient synthesi... |
|
|
Kinetic and spectroscopic studies of bicupin oxalate oxidase and putative active site mutants.
PLoS ONE 8(3) , e57933, (2013) Ceriporiopsis subvermispora oxalate oxidase (CsOxOx) is the first bicupin enzyme identified that catalyzes manganese-dependent oxidation of oxalate. In previous work, we have shown that the dominant contribution to catalysis comes from the monoprotonated form... |
|
|
Amino acids form strongly bound anions when substituted with superhalogen ligands.
J. Chem. Phys. 138(13) , 134310, (2013) The properties of AA-Y(-) anions (where AA = cysteine, aspartic acid, lysine; Y = BF3, PF5) were investigated at the ab initio Outer Valence Green's Function (OVGF)∕6-311++G(3df,3pd)∕∕MP2∕6-311++G(d,p) level of theory. It is shown that introducing a superhalo... |
|
|
Neutralisation of specific surface carboxylates speeds up translocation of botulinum neurotoxin type B enzymatic domain.
FEBS Lett. 587(23) , 3831-6, (2013) Botulinum neurotoxins translocate their enzymatic domain across vesicular membranes. The molecular triggers of this process are unknown. Here, we tested the possibility that this is elicited by protonation of conserved surface carboxylates. Glutamate-48, glut... |
|
|
Mechanism of transport modulation by an extracellular loop in an archaeal excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT) homolog.
J. Biol. Chem. 288(49) , 35266-76, (2013) Secondary transporters in the excitatory amino acid transporter family terminate glutamatergic synaptic transmission by catalyzing Na(+)-dependent removal of glutamate from the synaptic cleft. Recent structural studies of the aspartate-specific archaeal homol... |