| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
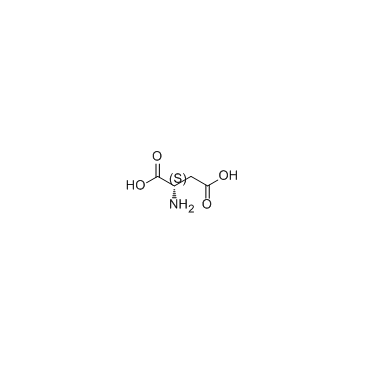 |
L-Aspartic acid
CAS:56-84-8 |
|
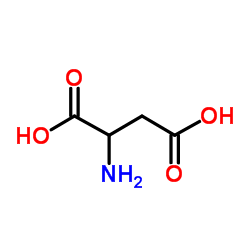 |
DL-Aspartic Acid
CAS:617-45-8 |
|
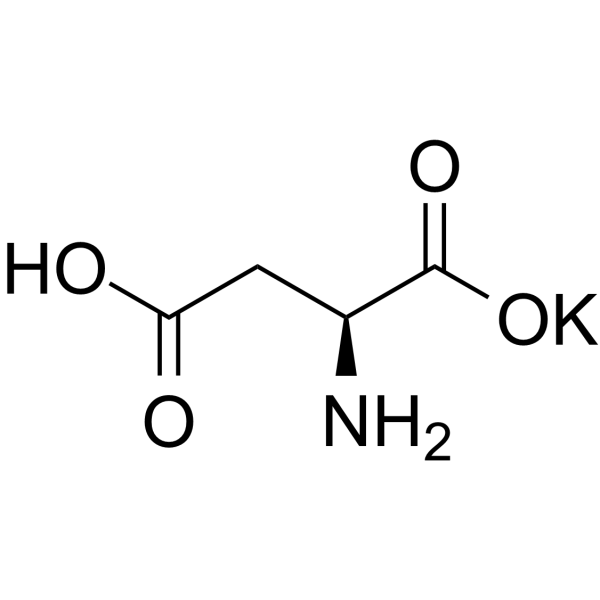 |
Butanedioate, 2-amino-, potassium salt (1:1)
CAS:1115-63-5 |
|
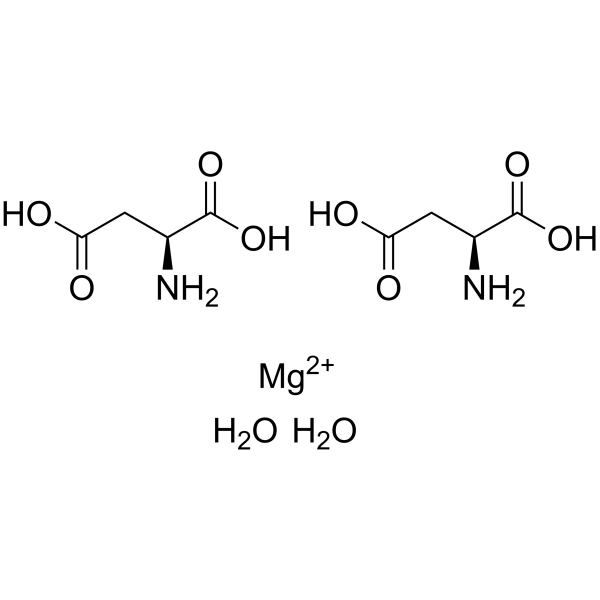 |
magnesium aspartate dihydrate
CAS:215533-00-9 |