Chloroacetaldehyde
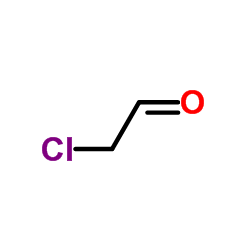
Chloroacetaldehyde structure
|
Common Name | Chloroacetaldehyde | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 107-20-0 | Molecular Weight | 78.498 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 85.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H3ClO | Melting Point | -28--23°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | -11.2±11.0 °C | |
| Symbol |




GHS05, GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Hydrolytic pathway of 5-fluorouracil in aqueous solutions for clinical use.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 98 , 446-62, (2014) The purpose of the study was to investigate the degradation pathway of 5-fluorouracil (FU) in the situation of commercial formulations for clinical use, namely FU dissolved in sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solutions or Tris buffer at pH 8.5-9. Combination of data f... |
|
|
Halogenated derivatives QSAR model using spectral moments to predict haloacetic acids (HAA) mutagenicity.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 5720-32, (2008) The risk of the presence of haloacetic acids in drinking water as chlorination by-products and the shortage of experimental mutagenicity data for most of them requires a research work. This paper describes a QSAR model to predict direct mutagenicity for these... |
|
|
Alkaline phosphatase protects against renal inflammation through dephosphorylation of lipopolysaccharide and adenosine triphosphate.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172 , 4932-45, (2015) Recently, two phase-II trials demonstrated improved renal function in critically ill patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury treated with the enzyme alkaline phosphatase. Here, we elucidated the dual active effect on renal protection of alkaline p... |
|
|
Nephron Toxicity Profiling via Untargeted Metabolome Analysis Employing a High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-based Experimental and Computational Pipeline.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 19121-32, (2015) Untargeted metabolomics has the potential to improve the predictivity of in vitro toxicity models and therefore may aid the replacement of expensive and laborious animal models. Here we describe a long term repeat dose nephrotoxicity study conducted on the hu... |
|
|
Plasma ATP is required for neutrophil activation in a mouse sepsis model.
Shock 42(2) , 142-7, (2014) Our previous work has shown that polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) require cellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) release and autocrine purinergic signaling for their activation. Here we studied in a mouse model of cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) whether ... |
|
|
Effects of chloroacetaldehyde in 2-chloroethanol-induced cardiotoxicity.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 49(5) , 1063-7, (2011) Cardiovascular effects have often been found in 2-chloroethanol (2-CE) intoxicated patients, but the 2-CE elicits cardiovascular toxicity mechanism is not clear. Recently, we have found that chloroacetaldehyde (CAA) accumulation in 2-CE-intoxicated rat's bloo... |
|
|
Protective effects of fomepizole on 2-chloroethanol toxicity.
Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 29(6) , 507-12, (2010) 2-Chloroethanol (2-CE) is a widely used industrial solvent. In Taiwan, Taiwanese farmers apply 2-CE on grape-vines to accelerate grape growth, a practice that in some cases have caused poisoning in humans. Thus, there is strong interest in identifying antidot... |
|
|
Protozoan ALKBH8 oxygenases display both DNA repair and tRNA modification activities.
PLoS ONE 9(6) , e98729, (2014) The ALKBH family of Fe(II) and 2-oxoglutarate dependent oxygenases comprises enzymes that display sequence homology to AlkB from E. coli, a DNA repair enzyme that uses an oxidative mechanism to dealkylate methyl and etheno adducts on the nucleobases. Humans h... |
|
|
Comparative metabolism of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide in the mouse using UPLC-ESI-QTOFMS-based metabolomics.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 80(7) , 1063-74, (2010) Ifosfamide (IF) and cyclophosphamide (CP) are common chemotherapeutic agents. Interestingly, while the two drugs are isomers, only IF treatment is known to cause nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity. Therefore, it was anticipated that a comparison of IF and CP dr... |
|
|
Investigation of ifosfamide nephrotoxicity induced in a liver-kidney co-culture biochip.
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 110(2) , 597-608, (2013) In this article, we present a liver-kidney co-culture model in a micro fluidic biochip. The liver was modeled using HepG2/C3a and HepaRG cell lines and the kidney using MDCK cell lines. To demonstrate the synergic interaction between both organs, we investiga... |