Chloroacetaldehyde
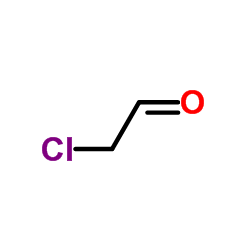
Chloroacetaldehyde structure
|
Common Name | Chloroacetaldehyde | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 107-20-0 | Molecular Weight | 78.498 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 85.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H3ClO | Melting Point | -28--23°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | -11.2±11.0 °C | |
| Symbol |




GHS05, GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | chloroacetaldehyde |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 85.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -28--23°C |
| Molecular Formula | C2H3ClO |
| Molecular Weight | 78.498 |
| Flash Point | -11.2±11.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 77.987244 |
| PSA | 17.07000 |
| LogP | 0.02 |
| Vapour Pressure | 70.6±0.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.382 |
| InChIKey | QSKPIOLLBIHNAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=CCCl |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |




GHS05, GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H310 + H330-H314-H335-H351-H400 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P280-P301 + P310 + P330-P303 + P361 + P353-P304 + P340 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T+:Verytoxic;N:Dangerous for the environment; |
| Risk Phrases | R24/25;R26;R34;R40;R50 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S28-S36/37/39-S45-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 2232 6.1/PG 1 |
| WGK Germany | - |
| RTECS | AB2450000 |
| Packaging Group | I |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| HS Code | 2913000090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2913000090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2913000090 halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives of products of heading 2912 Educational tariff:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Regulatory conditions:none Most favored nation tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Hydrolytic pathway of 5-fluorouracil in aqueous solutions for clinical use.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 98 , 446-62, (2014) The purpose of the study was to investigate the degradation pathway of 5-fluorouracil (FU) in the situation of commercial formulations for clinical use, namely FU dissolved in sodium hydroxide (NaOH) ... |
|
|
Halogenated derivatives QSAR model using spectral moments to predict haloacetic acids (HAA) mutagenicity.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 5720-32, (2008) The risk of the presence of haloacetic acids in drinking water as chlorination by-products and the shortage of experimental mutagenicity data for most of them requires a research work. This paper desc... |
|
|
Alkaline phosphatase protects against renal inflammation through dephosphorylation of lipopolysaccharide and adenosine triphosphate.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172 , 4932-45, (2015) Recently, two phase-II trials demonstrated improved renal function in critically ill patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury treated with the enzyme alkaline phosphatase. Here, we elucidat... |
| Acetaldehyde,chloro |
| EINECS 203-472-8 |
| MFCD00006992 |
| Acetaldehyde,2-chloro |
| chloromethyl-ketone |
| Chloroethanal |
| Chloroaldehyde |
| chloro-acetaldehyde |
| 2-Chloroethanal |
| 2-Chloro-1-ethanal |
 CAS#:621-62-5
CAS#:621-62-5 CAS#:79-11-8
CAS#:79-11-8 CAS#:107-07-3
CAS#:107-07-3 CAS#:97-97-2
CAS#:97-97-2 CAS#:3967-54-2
CAS#:3967-54-2 CAS#:79-04-9
CAS#:79-04-9 CAS#:1129-52-8
CAS#:1129-52-8 CAS#:107-21-1
CAS#:107-21-1 CAS#:107-05-1
CAS#:107-05-1 CAS#:4124-17-8
CAS#:4124-17-8![Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-8-methanol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/424/111477-17-9.png) CAS#:111477-17-9
CAS#:111477-17-9 CAS#:108153-93-1
CAS#:108153-93-1 CAS#:38401-67-1
CAS#:38401-67-1![Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-7-methanol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/308/342613-80-3.png) CAS#:342613-80-3
CAS#:342613-80-3 CAS#:496-15-1
CAS#:496-15-1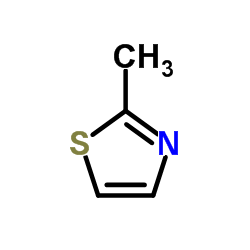 CAS#:3581-87-1
CAS#:3581-87-1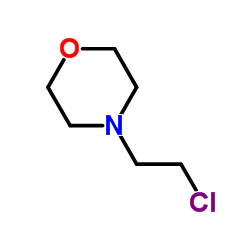 CAS#:3240-94-6
CAS#:3240-94-6 CAS#:141277-73-8
CAS#:141277-73-8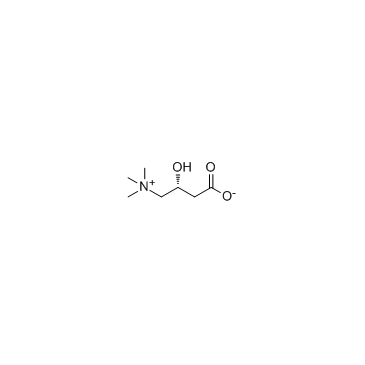 CAS#:541-15-1
CAS#:541-15-1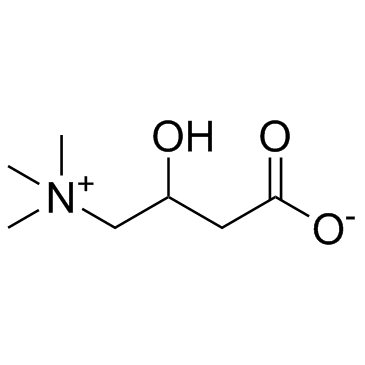 CAS#:406-76-8
CAS#:406-76-8
