Chlorophenol Red
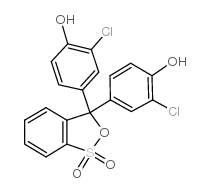
Chlorophenol Red structure
|
Common Name | Chlorophenol Red | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4430-20-0 | Molecular Weight | 423.26700 | |
| Density | 1.605g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 583ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H12Cl2O5S | Melting Point | 261 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 306.4ºC | |
|
Trypanocidal Activity of Long Chain Diamines and Aminoalcohols.
Molecules 20 , 11554-68, (2015) Thirteen aminoalcohols and eight diamines were obtained and tested against Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes strains MG, JEM and CL-B5 clone. Some of them were equal or more potent (1.0-6.6 times) than the reference compound nifurtimox. From them, three aminoal... |
|
|
Immune response profile elicited by the model antigen ovalbumin expressed in fusion with the bacterial OprI lipoprotein.
Mol. Immunol. 64(1) , 36-45, (2015) The use of immunogenic formulations targeting pattern recognition receptors towards modulation of immune responses is a promising strategy to develop better vaccines against infectious and malignant diseases. Molecules targeting TLR2 offer interesting propert... |
|
|
Enhancement of MHC-I antigen presentation via architectural control of pH-responsive, endosomolytic polymer nanoparticles.
AAPS J. 17(2) , 358-69, (2015) Protein-based vaccines offer a number of important advantages over organism-based vaccines but generally elicit poor CD8(+) T cell responses. We have previously demonstrated that pH-responsive, endosomolytic polymers can enhance protein antigen delivery to ma... |
|
|
Detection of marine microalgal biotoxins using bioassays based on functional expression of tunicate xenobiotic receptors in yeast.
Toxicon 95 , 13-22, (2015) Marine microalgae can produce biotoxins that cause widespread poisoning in marine ecosystems and may also affect human health. While established microalgal biotoxins are detectable using chemical methods, a need remains for robust, inexpensive bioassays. Liga... |
|
|
Human receptor activation by aroclor 1260, a polychlorinated biphenyl mixture.
Toxicol. Sci. 140(2) , 283-97, (2014) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are persistent environmental toxicants, present in 100% of U.S. adults and dose-dependently associated with obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). PCBs are predicted to interact with receptors previously implic... |
|
|
Azithromycin is able to control Toxoplasma gondii infection in human villous explants.
J. Transl. Med. 12 , 132, (2014) Although Toxoplasma gondii infection is normally asymptomatic, severe cases of toxoplasmosis may occur in immunosuppressed patients or congenitally infected newborns. When a fetal infection is established, the recommended treatment is a combination of pyrimet... |
|
|
Octaarginine-modified liposomes enhance cross-presentation by promoting the C-terminal trimming of antigen peptide.
Mol. Pharm. 11(8) , 2787-95, (2014) Exogenous antigen proteolysis by proteasomes and amino peptidases is essential for the production of mature major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) peptides to induce cross-presentation. We report here that when liposomes are modified with octaargini... |
|
|
Potential novel antibiotics from HTS targeting the virulence-regulating transcription factor, VirF, from Shigella flexneri.
J. Antibiot. 67(5) , 379-86, (2014) VirF is an AraC-type transcriptional regulator responsible for activating the transcription of virulence genes required for the intracellular invasion and cell-to-cell spread of Shigella flexneri. Gene disruption studies have validated VirF as a potential tar... |
|
|
Dipeptides catalyze rapid peptide exchange on MHC class I molecules.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112(1) , 202-7, (2015) Peptide ligand selection by MHC class I molecules, which occurs by iterative optimization, is the centerpiece of immunodominance in antiviral and antitumor immune responses. For its understanding, the molecular mechanisms of peptide binding and dissociation b... |