Azure A
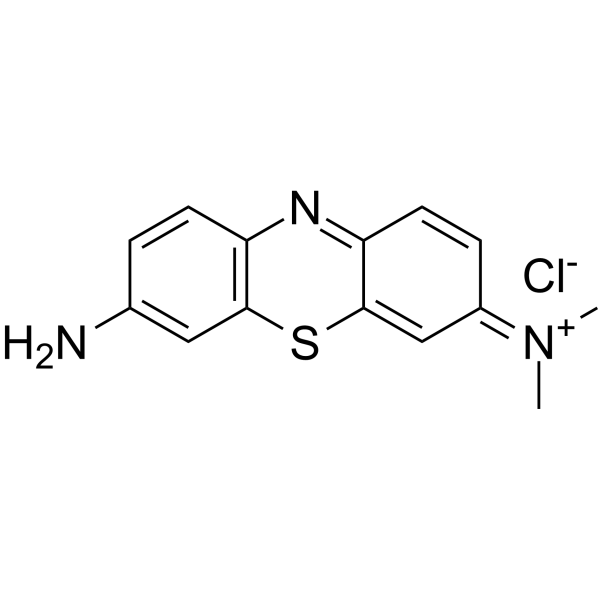
Azure A structure
|
Common Name | Azure A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 51811-82-6 | Molecular Weight | 291.799 | |
| Density | 0.99 | Boiling Point | 543ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H14ClN3S | Melting Point | 300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 15 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Redox effects and cytotoxic profiles of MJ25 and auranofin towards malignant melanoma cells.
Oncotarget 6 , 16488-506, (2015) Malignant melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer. Although recent progress in treatment has been achieved, lack of response, drug resistance and relapse remain major problems. The tumor suppressor p53 is rarely mutated in melanoma, yet it is inact... |
|
|
Coformer screening using thermal analysis based on binary phase diagrams.
Pharm. Res. 31(8) , 1946-57, (2014) The advent of cocrystals has demonstrated a growing need for efficient and comprehensive coformer screening in search of better development forms, including salt forms. Here, we investigated a coformer screening system for salts and cocrystals based on binary... |
|
|
Synthesis and characterization of copolyanhydrides of carbohydrate-based galactaric acid and adipic acid.
Carbohydr. Res. 402 , 102-10, (2014) A series of copolyanhydrides, consisting of 2,3,4,5-tetra-O-acetylgalactaric acid (AGA) and adipic acid (AA) as monomer units, was polymerized. Synthesis of AGA monomer consisted of two steps. First, O-acetylation of galactaric acid secondary hydroxyl groups ... |
|
|
Downregulation of Tryptophan-related Metabolomic Profile in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fluid.
J. Rheumatol. 42 , 2003-11, (2015) Synovial fluid (SF) is one of the most important materials that reflect the pathophysiological process of arthritis. A metabolomic and lipidomic study of SF was performed with the aim of identifying tentative diagnostic markers or therapeutic candidates for r... |
|
|
GC-MS analysis of organic acids in human urine in clinical settings: a study of derivatization and other analytical parameters.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 964 , 195-201, (2014) In the current paper the analytical conditions for the determination of ten free organic acids by GC-MS are studied with the aim to establish a method for organic acid profiling in human urine to be used as a tool for the detection of metabolic or other healt... |
|
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa exploits lipid A and muropeptides modification as a strategy to lower innate immunity during cystic fibrosis lung infection.
PLoS ONE 4(12) , e8439, (2009) Pseudomonas aeruginosa can establish life-long airways chronic infection in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) with pathogenic variants distinguished from initially acquired strain. Here, we analysed chemical and biological activity of P. aeruginosa Pathogen-... |
|
|
Filamin-interacting proteins, Cfm1 and Cfm2, are essential for the formation of cartilaginous skeletal elements.
Hum. Mol. Genet. 23(11) , 2953-67, (2014) Mutations of Filamin genes, which encode actin-binding proteins, cause a wide range of congenital developmental malformations in humans, mainly skeletal abnormalities. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying Filamin functions in skeletal system formation... |
|
|
Development of antimigraine transdermal delivery systems of pizotifen malate.
Int. J. Pharm. 492 , 223-32, (2015) The aim of this study was to develop and evaluate a transdermal delivery system of pizotifen malate. Pizotifen is frequently used in the preventive treatment of migraine, but is also indicated in eating disorders. In the course of the project, the effects of ... |
|
|
Effect of Excessive Potassium Iodide on Rat Aorta Endothelial Cells.
Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 166 , 201-9, (2015) The aim of the current study was to investigate the effect of excess iodine on rat aorta endothelial cells and the potential underlying mechanisms. Rat aorta endothelial cells were cultured with iodide ion (3506, 4076, 4647, 5218, 5789, 6360, 6931, and 7512 m... |
|
|
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells drive lymphangiogenesis.
PLoS ONE 9(9) , e106976, (2014) It is now well accepted that multipotent Bone-Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BM-MSC) contribute to cancer progression through several mechanisms including angiogenesis. However, their involvement during the lymphangiogenic process is poorly described. Using B... |