| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
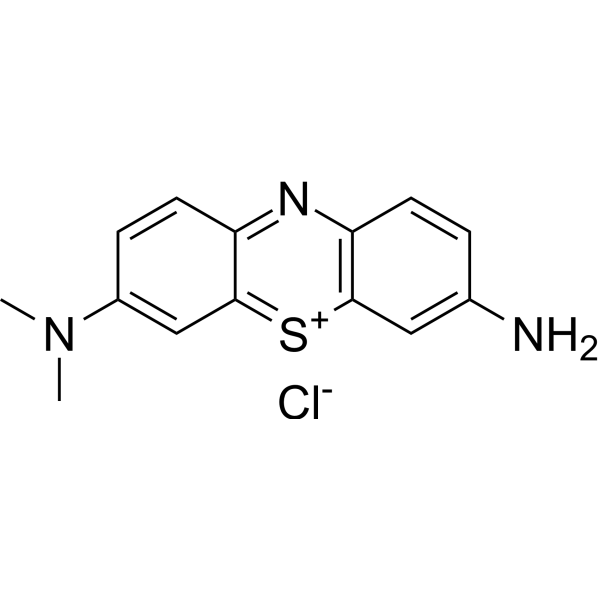 |
Azure A chloride
CAS:531-53-3 |
|
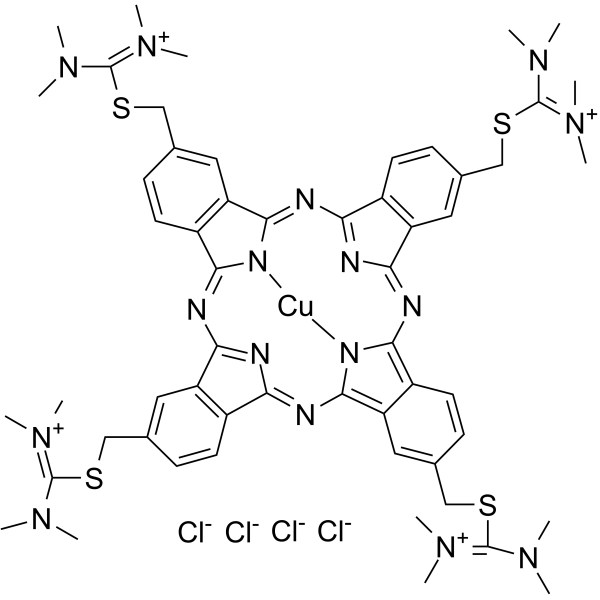 |
C.I. 74240
CAS:33864-99-2 |
|
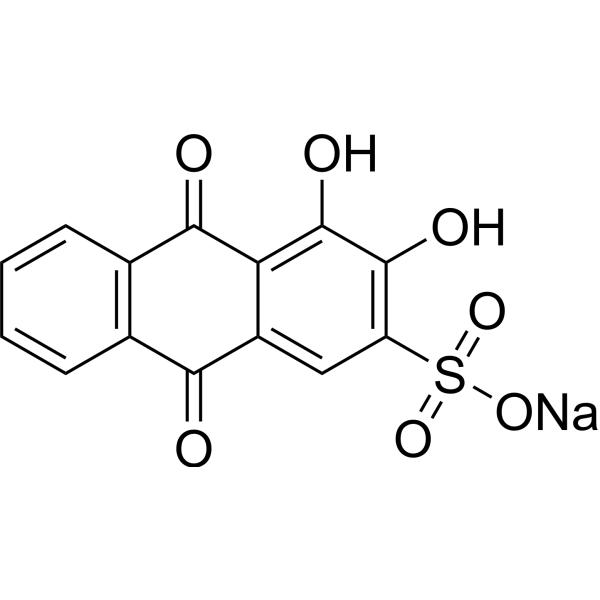 |
Alizarin red S
CAS:130-22-3 |
|
 |
Sodium selenite
CAS:10102-18-8 |
|
 |
toluidine blue for microscopy
CAS:6586-04-5 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
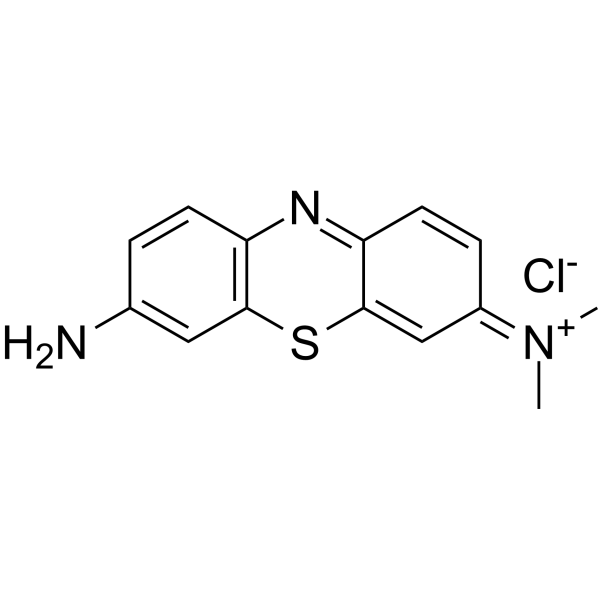 |
Azure A
CAS:51811-82-6 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |