Clindamycin phosphate
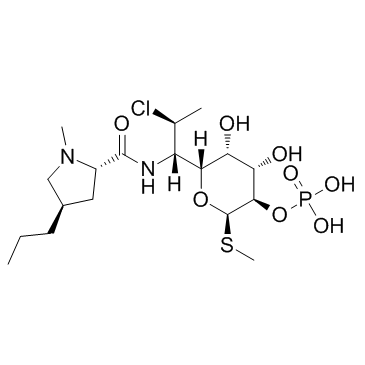
Clindamycin phosphate structure
|
Common Name | Clindamycin phosphate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 24729-96-2 | Molecular Weight | 504.963 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 159°C | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H34ClN2O8PS | Melting Point | 114ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Fungal recognition enhances mannose receptor shedding through dectin-1 engagement.
J. Biol. Chem. 286(10) , 7822-9, (2011) The mannose receptor (MR) is an endocytic type I membrane molecule with a broad ligand specificity that is involved in both hemostasis and pathogen recognition. Membrane-anchored MR is cleaved by a metalloproteinase into functional soluble MR (sMR) composed o... |
|
|
Enantioseparation of chiral acids and bases on a clindamycin phosphate-modified zirconia monolith by capillary electrochromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1251 , 244-8, (2012) Porous zirconia monolith modified with clindamycin phosphate (CLIP-ZM) was used as chiral stationary phase (CSP) to separate a set of six acidic and basic chiral compounds in capillary electrochromatography (CEC). Resolutions and chiral selectivity factors of... |
|
|
Enantioseparation of basic chiral compounds on a clindamycin phosphate-silica/zirconia hybrid monolith by capillary electrochromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1356 , 289-93, (2014) An organic-inorganic silica/zirconia hybrid monolithic capillary column was prepared by sol-gel process in a fused-silica capillary by using triethoxysilylpropylcarbamate (TEOSPC) derivative of clindamycin phosphate (CLIP) as a chiral selector. A sol solution... |
|
|
Efficacy of clindamycin hydrochloride capsules for the treatment of deep pyoderma due to Staphylococcus intermedius infection in dogs.
Can. Vet. J. 39(12) , 753-6, (1998) Clindamycin hydrochloride capsules (11 mg/kg body weight, q24 h) were administered orally to 20 dogs with deep staphylococcal pyoderma. Response to therapy was excellent in 100% of the dogs. Duration of therapy varied from 21 to 91 d, with an average duration... |
|
|
In vitro analysis of nanoparticulate hydroxyapatite/chitosan composites as potential drug delivery platforms for the sustained release of antibiotics in the treatment of osteomyelitis.
J. Pharm. Sci. 103(2) , 567-79, (2014) Nanoparticulate composites of hydroxyapatite (HAp) and chitosan were synthesized by ultrasound-assisted sequential precipitation and characterized for their microstructure at the atomic scale, surface charge, drug release properties, and combined antibacteria... |
|
|
Fulminant pseudomembranous colitis caused by clindamycin phosphate vaginal cream.
Am. J. Gastroenterol. 92(11) , 2112-3, (1997)
|
|
|
Clindamycin phosphate 1.2%- tretinoin 0.025% gel: vehicle characteristics, stability, and tolerability.
Cutis. 81(5) , 405-8, (2008) An aqueous gel formulation containing solubilized clindamycin phosphate 1.2% and a stable combination of both solubilized and crystalline tretinoin 0.025% (clin/tret) has been evaluated in 3 pivotal phase 3 studies, among other studies including a 52-week tri... |
|
|
Influence on mitochondria and cytotoxicity of different antibiotics administered in high concentrations on primary human osteoblasts and cell lines.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 54-63, (2007) Osteomyelitis, osteitis, spondylodiscitis, septic arthritis, and prosthetic joint infections still represent the worst complications of orthopedic surgery and traumatology. Successful treatment requires, besides surgical débridement, long-term systemic and hi... |
|
|
Comparison of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay with an Immunochromatographic Assay for Detection of Lincomycin in Milk and Honey.
Immunol. Invest. 44 , 438-50, (2015) An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and an immunochromatographic assay were constructed for the detection of lincomycin (LIN) in both milk and honey samples based on the monoclonal antibody named 5F6. The half-maximum inhibition of ELISA was 0.3 ng/m... |
|
|
Comparison of tretinoin 0.05% cream and 3% alcohol-based salicylic acid preparation in the treatment of acne vulgaris.
J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 25(3) , 328-33, (2011) No single effective topical treatment is available for treating all pathogenic factors causing acne vulgaris (AV). Salicylic acid (SA), tretinoin (all-TRA) and clindamycin phosphate (CDP) are known to to be effective agents depending on their comedolytic and ... |