CHLORO(TRIETHYLPHOSPHINE)GOLD(I)
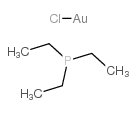
CHLORO(TRIETHYLPHOSPHINE)GOLD(I) structure
|
Common Name | CHLORO(TRIETHYLPHOSPHINE)GOLD(I) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 15529-90-5 | Molecular Weight | 350.57700 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 210ºC0.03 mm Hg(lit.) | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H15AuClP | Melting Point | 84-86ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 27.2ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Synthesis of thionato(triethylphosphine) gold(I) complexes:analogues of "auranofin," an antiarthritic drug.
J. Inorg. Biochem. 38(2) , 95-100, (1990) New compounds having the formula [L-Au-PEt3]Cl (where L = imidazolidine-2-thione(Imt) and 1,3-Diazinane-2-thione(Diaz)) are synthesized. They are characterized by elemental analysis, infrared, 13C and 31P NMR spectroscopy. |
|
|
Inhibition of human phospholipase C by aurothiomalate and (triethylphosphine) gold complexes.
Arzneimittelforschung 42(3) , 328-33, (1992) The effect of several gold complexes on the activity of phospholipase C from human blood platelets was studied in vitro. Aurothiomalate and auranofin--2 agents used for the chrysotherapy of rheumatoid arthritis--, gold chloride, (triethylphosphine)gold chlori... |
|
|
The structural flexibility of ferric cytochrome c: regulation of the spin-state equilibrium by an anti-arthritic gold(I) compound at neutral pH.
FEBS Lett. 116(2) , 227-30, (1980)
|
|
|
31P nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies at 24 and 162 MHz of blood containing an anti-arthritic gold phosphine: relaxation via chemical-shift anisotropy.
Biochem. Soc. Trans. 8(5) , 635-6, (1980)
|
|
|
Inhibition of human neutrophil collagenase by gold(I) salts used in chrysotherapy.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 144(1) , 101-8, (1987) Six gold(I) salts, some of which are used as drugs in chrysotherapy, are shown to be inhibitors of two forms of human neutrophil collagenase. The IC50 values vary over six orders of magnitude, the lowest being 3.5 nM for Myocrisin. Thus, inhibition is greatly... |
|
|
A comparison of the effects of two gold-containing therapeutic agents on articular chondrocyte growth in vitro.
Rheumatol. Int. 3(2) , 49-56, (1983) Chondrocyte structure and function under the influence of two gold-containing therapeutic agents, aurothioglucose and triethylphosphine gold, were studied in a monolayer culture system for cultivating lapine articular chondrocytes. The functional parameters i... |
|
|
Effects of gold compounds on the function of phagocytic cells. II. Inhibition of superoxide radical generation by tripeptide-activated polymorphonuclear leukocytes.
Arthritis Rheum. 26(1) , 82-6, (1983) The effect of sodium aurothiomalate and triethylphosphine gold on the generation of superoxide radicals by chemotactic tripeptide-activated polymorphonuclear leukocytes has been investigated using a cytochrome C reduction technique. Neither gold compound inhi... |
|
|
The comparative toxicity of gold salts.
J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 8 , 79-80, (1982)
|
|
|
Cellular and molecular pharmacology of auranofin and related gold complexes.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 35(20) , 3423-31, (1986)
|
|
|
The mechanism of acute cytotoxicity of triethylphosphine gold(I) complexes. II. Triethylphosphine gold chloride-induced alterations in mitochondrial function.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 90(3) , 391-400, (1987) Triethylphosphine gold complexes have therapeutic activity in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Many of these compounds are also highly cytotoxic in vitro to a variety of tumor and non-tumor cell lines. Triethylphosphine gold chloride (TEPAu) is highly c... |