pyridostigmine bromide
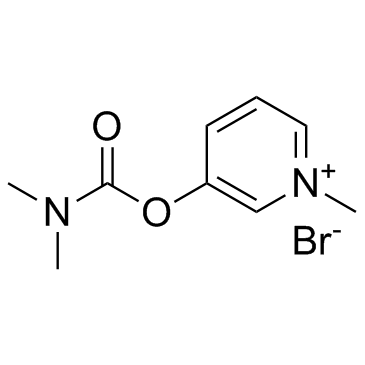
pyridostigmine bromide structure
|
Common Name | pyridostigmine bromide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 101-26-8 | Molecular Weight | 261.116 | |
| Density | 0.9613 g/cm3 (20ºC) | Boiling Point | 88 (25 torr) | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H13BrN2O2 | Melting Point | 154 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Gulf War agent exposure causes impairment of long-term memory formation and neuropathological changes in a mouse model of Gulf War Illness.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0119579, (2015) Gulf War Illness (GWI) is a chronic multisymptom illness with a central nervous system component such as memory deficits, neurological, and musculoskeletal problems. There are ample data that demonstrate that exposure to Gulf War (GW) agents, such as pyridost... |
|
|
Gingival pain: an unusual side effect of ziprasidone.
BMJ Case Rep. 2013 , doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007577, (2013) The patient is a 52-year-old man with schizophrenia who developed severe, unremitting gingival pain after his ziprasidone dosage was increased from 80 to 120 mg. His physical examination and laboratory findings were unremarkable. He did not have any extra-pyr... |
|
|
4R-cembranoid protects against diisopropylfluorophosphate-mediated neurodegeneration.
Neurotoxicology 44 , 80-90, (2014) Many organophosphorous esters synthesized for applications in industry, agriculture, or warfare irreversibly inhibit acetylcholinesterase, and acute poisoning with these compounds causes life-threatening cholinergic overstimulation. Following classical emerge... |
|
|
Novel taste-masked orally disintegrating tablets for a highly soluble drug with an extremely bitter taste: design rationale and evaluation.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 39(9) , 1364-71, (2013) The purpose of this study was to evaluate the taste masking potential of novel solid dispersions (SDs) using Eudragit® EPO as the excipient when incorporated into the orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) for delivering a highly soluble drug with an extremely ... |
|
|
Alterations in gills of Lepomis gibbosus, after acute exposure to several xenobiotics (pesticide, detergent and pharmaceuticals): morphometric and biochemical evaluation.
Drug Chem. Toxicol. 38 , 126-32, (2015) In recent decades, scientific research about the effects of anthropogenic xenobiotics on non-target organisms has increased. Among the likely effects, some studies reported the evaluation of biochemical and morphological changes in specific tissues or organs ... |
|
|
Clinical features of congenital myasthenic syndrome due to mutations in DPAGT1.
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 84(10) , 1119-25, (2013) A newly defined congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) caused by DPAGT1 mutations has recently been reported. While many other CMS-associated proteins have discrete roles localised to the neuromuscular junction, DPAGT1 is ubiquitously expressed, modifying many ... |
|
|
Treatment in Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome.
Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1275 , 78-84, (2012) Besides antitumor therapy for patients with the paraneoplastic form of Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS), the mainstay of symptomatic treatment in LEMS is 3,4-diaminopyridine (3,4-DAP). Data from four randomized, placebo-controlled trials have revealed... |
|
|
GFPT1-myasthenia: clinical, structural, and electrophysiologic heterogeneity.
Neurology 81(4) , 370-8, (2013) To identify patients with GFPT1-related limb-girdle myasthenia and analyze phenotypic consequences of the mutations.We performed genetic analysis, histochemical, immunoblot, and ultrastructural studies and in vitro electrophysiologic analysis of neuromuscular... |
|
|
Flow-through enzyme immobilized amperometric detector for the rapid screening of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors by flow injection analysis.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 102 , 267-75, (2015) A commercially available thin-layer flow-through amperometric detector, with the sensing block customized in an original design, was applied to the screening of drug compounds known as acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors. AChE from electric eel was covalen... |
|
|
Chronic cholinergic stimulation promotes changes in cardiovascular autonomic control in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Auton. Neurosci. 193 , 97-103, (2015) Hypertension is often accompanied by autonomic dysfunction, which is detrimental to cardiac regulation. On the other hand, cholinergic stimulation through inhibition of acetylcholinesterase appears to have beneficial effects on cardiac autonomic control. Thus... |