α-maltotriose
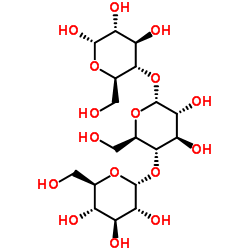
α-maltotriose structure
|
Common Name | α-maltotriose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9005-82-7 | Molecular Weight | 504.437 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 865.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H30O16 | Melting Point | 273ºC-275ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 477.0±34.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Morphology and structural properties of high-amylose rice starch residues hydrolysed by amyloglucosidase.
Food Chem. 138(4) , 2089-98, (2013) High-amylose starches are attracting considerable attention because of their potential health benefits and industrial uses. Enzyme hydrolysis of starch is involved in many biological and industrial processes. In this paper, starches were isolated from high-am... |
|
|
Formation of resistant corn starches induced by gamma-irradiation.
Carbohydr. Polym. 97(2) , 614-7, (2013) The effect of gamma-irradiation on formation of resistant starch (RS) in corn starch with different amylose content was examined. Normal corn starch, waxy corn starch, and high amylose corn starch (Hylon V and Hylon VII) were irradiated at 5, 10, 25 and 50 kG... |
|
|
Dietary resistant starch prevents urinary excretion of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol and vitamin D-binding protein in type 1 diabetic rats.
J. Nutr. 143(7) , 1123-8, (2013) Diabetes is a rapidly growing epidemic affecting millions of Americans and has been implicated in a number of devastating secondary complications. We previously demonstrated that type 2 diabetic rats exhibit vitamin D deficiency due to aberrant megalin-mediat... |
|
|
Microstructure and characteristics of high-amylose corn starch-chitosan film as affected by composition.
Food Sci. Technol. Int. 19(3) , 279-87, (2013) Edible films composed of high-amylose corn starch and chitosan were developed by casting method. The effects of the ratio of high-amylose corn starch to chitosan, concentration of glycerol and methyl cellulose on the oxygen and carbon dioxide permeation, wate... |
|
|
Chemical composition and functional properties of native chestnut starch (Castanea sativa Mill).
Carbohydr. Polym. 94(1) , 594-602, (2013) Starch isolation methods can change their physico-chemical and functional characteristics hindering the establishment of a starch-food functionality relation. A simple high yield and soft isolation method was applied for chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill) starch... |
|
|
Enzymatic transformation of nonfood biomass to starch.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(18) , 7182-7, (2013) The global demand for food could double in another 40 y owing to growth in the population and food consumption per capita. To meet the world's future food and sustainability needs for biofuels and renewable materials, the production of starch-rich cereals and... |
|
|
Effect of the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate on the phase transition of starch: dissolution or gelatinization?
Carbohydr. Polym. 94(1) , 520-30, (2013) This work revealed that the interactions between starch, the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate ([Emim][OAc]), and water might contribute to the phase transition (gelatinization, dissolution, or both) of native starch at reduced temperature. Usi... |
|
|
Molecular order and functional properties of starches from three waxy wheat varieties grown in China.
Food Chem. 181 , 43-50, (2015) Molecular order and functional properties of starch from three waxy wheat varieties grown in China were investigated by a combination of various technical analyses. The total starch content of the waxy wheat ranged between 54.1% and 55.0%, and the amylose con... |
|
|
Dielectric studies of amylose, amylopectin and amylose-stearic acid complexes.
Carbohydr. Polym. 92(2) , 1530-8, (2013) The effect of structure creation and moisture content on the dielectric properties of amylose, amylopectin and amylose-stearic acid complexes is presented. Three dielectric features have been identified in these systems. At low temperature, a dipole relaxatio... |
|
|
Retention models and interaction mechanisms of acetone and other carbonyl-containing molecules with amylose tris[(S)-α-methylbenzylcarbamate] sorbent.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1279 , 36-48, (2013) The stoichiometric displacement models developed in the literature have been widely used for understanding the adsorption mechanisms of solutes in various chromatography systems. The models were used to explain the linear plots of the logarithms of the solute... |