Adenine
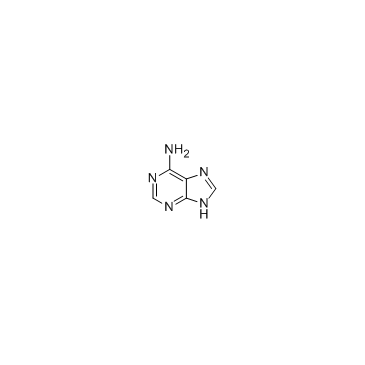
Adenine structure
|
Common Name | Adenine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 73-24-5 | Molecular Weight | 135.127 | |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 243.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H5N5 | Melting Point | 360-365ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 100.9±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Multifactorial analysis of conditional reprogramming of human keratinocytes.
PLoS ONE 10(2) , e0116755, (2015) Co-culture of human primary epithelial cells with irradiated 3T3 fibroblast feeder cells (J2 cells) and the Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (Y) allows for the unrestricted growth of cells of epithelial origin by the process termed conditional reprogramming. To b... |
|
|
Vegetables' juice influences polyol pathway by multiple mechanisms in favour of reducing development of oxidative stress and resultant diabetic complications.
Pharmacogn. Mag. 10(Suppl 2) , S383-91, (2014) Hyperglycemia induced generation of free radicals and consequent development of oxidative stress by polyol pathway is one of the crucial mechanisms stirring up development of diabetic complications. We evaluated influence of ten vegetables' juice on polyol pa... |
|
|
Dynamic switching of active promoter and enhancer domains regulates Tet1 and Tet2 expression during cell state transitions between pluripotency and differentiation.
Mol. Cell. Biol. 35(6) , 1026-42, (2015) The Tet 5-methylcytosine dioxygenases catalyze DNA demethylation by producing 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and further oxidized products. Tet1 and Tet2 are highly expressed in mouse pluripotent cells and downregulated to different extents in somatic cells, but the... |
|
|
Monitoring F1651 P-like fimbria expression at the single-cell level reveals a highly heterogeneous phenotype.
Infect. Immun. 83(5) , 1929-39, (2015) F1651 and the pyelonephritis-associated pili (Pap) are two members of the type P family of adhesive factors. They play a key role in establishing disease caused by extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) strains in animals and humans. Both F1651 a... |
|
|
Perturbation of the monomer-monomer interfaces of the benzoylformate decarboxylase tetramer.
Biochemistry 53(27) , 4358-67, (2014) The X-ray structure of benzoylformate decarboxylase (BFDC) from Pseudomonas putida ATCC 12633 shows it to be a tetramer. This was believed to be typical of all thiamin diphosphate-dependent decarboxylases until recently when the structure of KdcA, a branched-... |
|
|
Hypoxanthine uptake by skeletal muscle microvascular endothelial cells from equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (ENT1)-null mice: effect of oxidative stress.
Microvasc. Res. 98 , 16-22, (2015) Adenosine is an endogenous regulator of vascular tone. This activity of adenosine is terminated by its uptake and metabolism by microvascular endothelial cells (MVEC). The predominant transporter involved is ENT1 (equilibrative nucleoside transporter subtype ... |
|
|
Oxidative stress modulates nucleobase transport in microvascular endothelial cells
Microvasc. Res. 95 , 68-75, (2014) Purine nucleosides and nucleobases play key roles in the physiological response to vascular ischemia/reperfusion events. The intra- and extracellular concentrations of these compounds are controlled, in part, by equilibrative nucleoside transporter subtype 1 ... |
|
|
Metabolic study of androsta-1,4,6-triene-3,17-dione in horses using liquid chromatography/high resolution mass spectrometry.
J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 152 , 142-54, (2015) Androsta-1,4,6-triene-3,17-dione (ATD) is an irreversible steroidal aromatase inhibitor and is marketed as a supplement. It has been reported to effectively reduce estrogen biosynthesis and significantly increase the levels of endogenous steroids such as dihy... |
|
|
Size and molecular flexibility of sugars determine the storage stability of freeze-dried proteins.
Mol. Pharm. 12(3) , 684-94, (2015) Protein-based biopharmaceuticals are generally produced as aqueous solutions and stored refrigerated to obtain sufficient shelf life. Alternatively, proteins may be freeze-dried in the presence of sugars to allow storage stability at ambient conditions for pr... |
|
|
Identification of critical ligand binding determinants in Mycobacterium tuberculosis adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate reductase.
J. Med. Chem. 52 , 5485-95, (2009) Mycobacterium tuberculosis adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (APS) reductase is an iron-sulfur protein and a validated target to develop new antitubercular agents, particularly for the treatment of latent infection. To facilitate the development of potent and speci... |