naftalofos
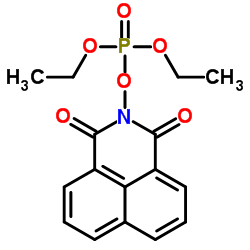
naftalofos structure
|
Common Name | naftalofos | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1491-41-4 | Molecular Weight | 349.275 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 487.3±28.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H16NO6P | Melting Point | 115-116ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 248.5±24.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Phenobarbital induction and chemical synergism demonstrate the role of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases in detoxification of naphthalophos by Haemonchus contortus larvae.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(12) , 7475-83, (2014) We used an enzyme induction approach to study the role of detoxification enzymes in the interaction of the anthelmintic compound naphthalophos with Haemonchus contortus larvae. Larvae were treated with the barbiturate phenobarbital, which is known to induce t... |
|
|
The efficacy of trichlorphon and naphthalophos against multiple anthelmintic-resistant nematodes of naturally infected sheep in Argentina.
Parasitol. Res. 109 Suppl 1 , S139-48, (2011) An anthelmintic efficacy trial was conducted in sheep harbouring anthelmintic-resistant worms in Argentina. Seventy lambs were selected from a flock that had been grazed on pastures infected with trichostrongyles previously shown to be resistant to the main a... |
|
|
Pharmacology of anthelmintic resistance.
Parasitology 113 Suppl , S201-16, (1996) Anthelmintic resistance has compromised the control of nematode parasites in several animal-based industries. Studies of resistance have not only improved our understanding of this phenomenon but also shed light on physiological systems of parasitic helminths... |
|
|
Characterization of moxidectin resistant Trichostrongylus colubriformis and Haemonchus contortus.
Vet. Parasitol. 128(1-2) , 83-90, (2005) The development of moxidectin resistance (MOX-R) in sheep parasitic gastrointestinal nematodes already carrying multiple resistances to other anthelmintic groups has made control of these strains very difficult. The anthelmintic resistance patterns of MOX-R s... |
|
|
Mixtures of anthelmintics: a strategy against resistance.
Aust. Vet. J. 65(2) , 62-4, (1988)
|
|
|
Investigation of intestinal nematode responses to naphthalophos and pyrantel using a larval development assay.
Int. J. Parasitol. 29(7) , 1093-9, (1999) Responses of several nematode species to naphthalophos and pyrantel/levamisole were examined using a larval development assay in order to determine the potential of this assay for detection of resistance. Haemonchus contortus and Ostertagia circumcincta showe... |
|
|
Multiple anthelmintic resistance in Trichostrongylus colubriformis.
Aust. Vet. J. 63(2) , 45-7, (1986) Following the failure of anthelmintic treatment to control an outbreak of trichostrongylosis in sheep, multiple resistance to levamisole and oxfendazole was confirmed in field strains of Trichostrongylus colubriformis at the CSIRO Pastoral Research Laboratory... |
|
|
Naphthalophos combinations with benzimidazoles or levamisole as effective anthelmintics for sheep.
Aust. Vet. J. 74(3) , 221-4, (1996) To investigate the relative efficacy and safety of the anthelmintic naphthalophos in sheep, either given alone or in combination with benzimidazole (fenbendazole and albendazole) or levamisole anthelmintics.A parasitological study using faecal egg count reduc... |
|
|
The effect of the intestinal worms and migrating L1 larvae of Trichinella spiralis on the production of antiparasitic IgE antibodies.
Parasitol. Res. 74(6) , 581-5, (1988) The effect of the adult worms and migrating L1 larvae of Trichinella spiralis on the production of specific IgE antibodies was determined in BCF1 mice. To achieve this, we combined the effect of two anthelminthics: thiabendazole, to produce chemosterilization... |