Isovanillic acid
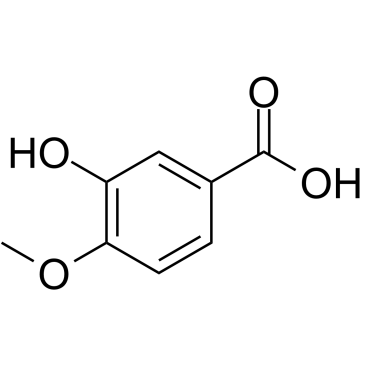
Isovanillic acid structure
|
Common Name | Isovanillic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 645-08-9 | Molecular Weight | 168.147 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 344.3±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8O4 | Melting Point | 250-253 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 145.2±17.2 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Structure-Activity Relationships of Antimicrobial Gallic Acid Derivatives from Pomegranate and Acacia Fruit Extracts against Potato Bacterial Wilt Pathogen.
Chem. Biodivers. 12 , 955-62, (2015) Bacterial wilts of potato, tomato, pepper, and or eggplant caused by Ralstonia solanacearum are among the most serious plant diseases worldwide. In this study, the issue of developing bactericidal agents from natural sources against R. solanacearum derived fr... |
|
|
Mass spectrometric behavior of phenolic acids standards and their analysis in the plant samples with LC/ESI/MS system.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 967 , 21-7, (2014) Liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (MS) with electrospray ionization (ESI) is one of analytical techniques to obtain accurate results of low molecular weight aromatic compounds in biological samples of different origin. The interpretations of ... |
|
|
Flavonoid metabolites reduce tumor necrosis factor-α secretion to a greater extent than their precursor compounds in human THP-1 monocytes.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 59 , 1143-54, (2015) Flavonoids are generally studied in vitro, in isolation, and as unmetabolized precursor structures. However, in the habitual diet, multiple flavonoids are consumed together and found present in the circulation as complex mixtures of metabolites. Using a uniqu... |
|
|
[Study on the chemical constituents of Phryma leptostachya].
Zhong Yao Cai 34(9) , 1368-70, (2011) To study the chemical constituents of Phryma leptostachya.The chemical constituents were isolated and purified by silica gel column, recrystallization and Pre-RP-HPLC and their structwes were elucidated by spectroscopic methods.Five compounds were obtained an... |
|
|
O-demethylation by the homoacetogenic anaerobe Holophaga foetida studied by a new photometric methylation assay using electrochemically produced cob(I)alamin.
Eur. J. Biochem. 226(3) , 945-51, (1994) The previously studied complete methyl transfer sequence of tetrahydrofolate-dependent O-demethylation catalyzed by Holophaga foetida strain TMBS4 extracts was separated into two steps using cobalamins as non-physiological substrates: electrochemically produc... |
|
|
Production of methanol from aromatic acids by Pseudomonas putida.
J. Bacteriol. 142(3) , 916-24, (1980) When grown at the expense of 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid, a strain of Pseudomonas putida oxidized this compound and also 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic (syringic) and 3,4-dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic (3-O-methylgallic) acids; but other hydroxy- or methoxy-benz... |
|
|
Metabolism of isovanillate, vanillate, and veratrate by Comamonas testosteroni strain BR6020.
J. Bacteriol. 188(11) , 3862-9, (2006) In Comamonas testosteroni strain BR6020, metabolism of isovanillate (iVan; 3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoate), vanillate (Van; 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate), and veratrate (Ver; 3,4-dimethoxybenzoate) proceeds via protocatechuate (Pca; 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate). A 13.4... |
|
|
Substrate-induction of veratric acid O-demethylase in Nocardia sp.
Acta Biochim. Pol. 31(4) , 383-95, (1984) Nocardia sp. demethylates veratric acid to vanillic and isovanillic acids, and subsequently to protocatechuic acid. The accumulation of specific mRNA observed during incubation of Nocardia sp. cells with substrate, as well as the effect of inhibitors of trans... |
|
|
Isolation and characterization of Streptomyces sp. NL15-2K capable of degrading lignin-related aromatic compounds.
J. Biosci. Bioeng. 102(2) , 124-7, (2006) Strain NL15-2K was isolated from soil by screening for bacteria capable of catabolizing lignin-related aromatic acids. This isolate was identified as a Streptomyces sp. on the basis of morphology and an analysis of its 16S rRNA gene sequence. NL15-2K utilized... |
|
|
Metabolism of isovanillin by aldehyde oxidase, xanthine oxidase, aldehyde dehydrogenase and liver slices.
Pharmacology 73(4) , 199-208, (2005) Aromatic aldehydes are good substrates of aldehyde dehydrogenase activity but are relatively poor substrates of aldehyde oxidase and xanthine oxidase. However, the oxidation of xenobiotic-derived aromatic aldehydes by the latter enzymes has not been studied t... |