Caffeic acid
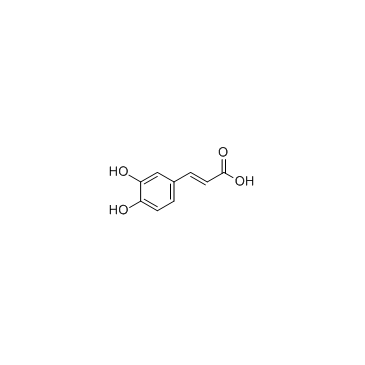
Caffeic acid structure
|
Common Name | Caffeic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 331-39-5 | Molecular Weight | 180.157 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 416.8±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O4 | Melting Point | 211-213 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 220.0±22.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Antimicrobial activity of natural products from the flora of Northern Ontario, Canada.
Pharm. Biol. 53(6) , 800-6, (2015) The number of multidrug resistant (MDR) microorganisms is increasing and the antimicrobial resistance expressed by these pathogens is generating a rising global health crisis. In fact, there are only a few antimicrobial agents left that can be used against MD... |
|
|
The hepatoprotection of caffeic acid and rosmarinic acid, major compounds of Perilla frutescens, against t-BHP-induced oxidative liver damage.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 55 , 92-9, (2013) Perilla frutescens leaves are often used in East Asian gourmet food. In this study, we investigated the hepatoprotective effects of caffeic acid (CA), rosmarinic acid (RA), and their combination. P. frutescens contains 1.32μg CA/mg dry material (DM) and 26.84... |
|
|
Effect of selected Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains and different aging techniques on the polysaccharide and polyphenolic composition and sensorial characteristics of Cabernet Sauvignon red wines.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95 , 2132-44, (2015) The objective of this work was to study the effect of two Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains with different capabilities of polysaccharide liberation during alcoholic fermentation in addition to subsequent aging on lees with or without oak wood chips as w... |
|
|
15-Lipoxygenase-1 suppression of colitis-associated colon cancer through inhibition of the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway.
FASEB J. 29 , 2359-70, (2015) The IL-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway is a critical signaling pathway for colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CAC). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-δ, a lipid nuclear receptor, up-regulates IL-6. 15-Li... |
|
|
Effects of UV exclusion on the physiology and phenolic composition of leaves and berries of Vitis vinifera cv. Graciano.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95(2) , 409-16, (2014) Ultraviolet (UV) radiation induces adaptive responses that can be used for plant production improvement. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of solar UV exclusion on the physiology and phenolic compounds of leaves and berry skins of Vitis vinifera ... |
|
|
Phenolic profiling in the pulp and peel of nine plantain cultivars (Musa sp.).
Food Chem. 167 , 197-204, (2014) The present study investigated the phenolic profiles of the pulp and peel of nine plantain cultivars and compared them to those of two dessert bananas of commercial interest (Grand Nain and Gros Michel), alongside a newly created hybrid, resistant to black si... |
|
|
[Chemical constituents from Commelina communis].
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 38(19) , 3304-8, (2013) To investigate the chemical constituents from Commelina communis, fifteen compounds were separated and purified by silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, and ODS column chromatography, and semi-preparative HPLC. By analyses of NMR and MS data as well as their physical a... |
|
|
Comparison between ATR-IR, Raman, concatenated ATR-IR and Raman spectroscopy for the determination of total antioxidant capacity and total phenolic content of Chinese rice wine.
Food Chem. 194 , 671-9, (2015) The application of attenuated total reflectance infrared spectroscopy (ATR-IR), Raman spectroscopy (RS) and combination of ATR-IR and RS for measurements of total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and total phenolic content (TPC) of Chinese rice wine (CRW) were inve... |
|
|
Isolation and characterization of feruloylated arabinoxylan oligosaccharides from the perennial cereal grain intermediate wheat grass (Thinopyrum intermedium).
Carbohydr. Res. 407 , 16-25, (2015) In comparison to the annual grain crops dominating current agricultural production, perennial grain species require fewer chemical and energy inputs and improve soil health and erosion control. The possibility for producing sustainable grain harvests from mar... |
|
|
Functional Characterization of Cucurbitadienol Synthase and Triterpene Glycosyltransferase Involved in Biosynthesis of Mogrosides from Siraitia grosvenorii.
Plant Cell Physiol. 56 , 1172-82, (2015) Mogrosides, the major bioactive components isolated from the fruits of Siraitia grosvenorii, are a family of cucurbitane-type tetracyclic triterpenoid saponins that are used worldwide as high-potency sweeteners and possess a variety of notable pharmacological... |