Prednisone
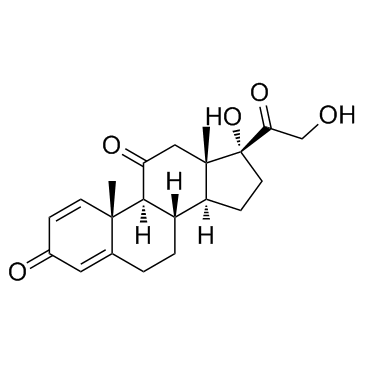
Prednisone structure
|
Common Name | Prednisone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 53-03-2 | Molecular Weight | 358.428 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 573.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H26O5 | Melting Point | 236-238 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 314.8±26.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Gold(I) complexes of 9-deazahypoxanthine as selective antitumor and anti-inflammatory agents.
PLoS ONE 9(10) , e109901, (2014) The gold(I) mixed-ligand complexes involving O-substituted derivatives of 9-deazahypoxanthine (HLn) and triphenylphosphine (PPh3) with the general formula [Au(Ln)(PPh3)] (1-5) were prepared and thoroughly characterized by elemental analysis, FT-IR and multinu... |
|
|
Development and validation of a new stability indicating reversed phase liquid chromatographic method for the determination of prednisolone acetate and impurities in an ophthalmic suspension.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 102 , 261-6, (2015) A new stability indicating reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) method was developed and validated under current International Conference of Harmonisation (ICH) guidance for the determination of prednisolone acetate (PAC) and impuri... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Detection and characterization of prednisolone metabolites in human urine by LC-MS/MS.
J. Mass Spectrom. 50(3) , 633-42, (2015) Glucocorticosteroids are prohibited in sports when used by systemic administrations (e.g. oral), whereas they are allowed using other administration ways. Strategies to discriminate between administrations routes have to be developed by doping control laborat... |
|
|
A kinetic study of the main guaco metabolites using syrup formulation and the identification of an alternative route of coumarin metabolism in humans.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0118922, (2015) For decades guaco species have been empirically used for the treatment of respiratory diseases. However, studies have shown that the toxic and therapeutic effects of the main guaco metabolites are dose-dependent, and none clinical study was done to evaluate t... |
|
|
Systematic evaluation of commercially available ultra-high performance liquid chromatography columns for drug metabolite profiling: optimization of chromatographic peak capacity.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1374 , 122-33, (2014) The present study investigated the practical use of modern ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) separation techniques for drug metabolite profiling, aiming to develop a widely applicable, high-throughput, easy-to-use chromatographic method, wi... |
|
|
Success with single-agent immunosuppression for multifocal choroidopathies.
Am. J. Ophthalmol. 158(6) , 1310-7, (2014) To evaluate the success of single-agent immunosuppression for patients with the posterior uveitides, birdshot chorioretinitis, multifocal choroiditis with panuveitis, and punctate inner choroiditis.Retrospective case series.setting: Tertiary care uveitis prac... |