(Z,E)-phytol
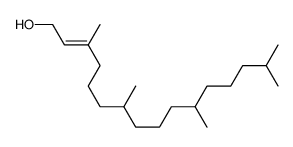
(Z,E)-phytol structure
|
Common Name | (Z,E)-phytol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7541-49-3 | Molecular Weight | 296.53100 | |
| Density | 0.85 g/mL at 25ºC(lit.) | Boiling Point | 202 - 205ºC at 15 hPa | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H40O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 187ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
MUCILAGE-RELATED10 Produces Galactoglucomannan That Maintains Pectin and Cellulose Architecture in Arabidopsis Seed Mucilage.
Plant Physiol. 169 , 403-20, (2015) Plants invest a lot of their resources into the production of an extracellular matrix built of polysaccharides. While the composition of the cell wall is relatively well characterized, the functions of the individual polymers and the enzymes that catalyze the... |
|
|
The presence of fucogalactoxyloglucan and its synthesis in rice indicates conserved functional importance in plants.
Plant Physiol. 168 , 549-60, (2015) The predominant structure of the hemicellulose xyloglucan (XyG) found in the cell walls of dicots is a fucogalactoXyG with an XXXG core motif, whereas in the Poaceae (grasses and cereals), the structure of XyG is less xylosylated (XXGGn core motif) and lacks ... |
|
|
13C Tracking after 13CO2 Supply Revealed Diurnal Patterns of Wood Formation in Aspen.
Plant Physiol. 168 , 478-89, (2015) Wood of trees is formed from carbon assimilated in the photosynthetic tissues. Determining the temporal dynamics of carbon assimilation, subsequent transport into developing wood, and incorporation to cell walls would further our understanding of wood formati... |
|
|
SENESCENCE-SUPPRESSED PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE Directly Interacts with the Cytoplasmic Domain of SENESCENCE-ASSOCIATED RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE and Negatively Regulates Leaf Senescence in Arabidopsis.
Plant Physiol. 169 , 1275-91, (2015) Reversible protein phosphorylation mediated by protein kinases and phosphatases plays an important role in the regulation of leaf senescence. We previously reported that the leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase SENESCENCE-ASSOCIATED RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE (... |
|
|
The MYB182 protein down-regulates proanthocyanidin and anthocyanin biosynthesis in poplar by repressing both structural and regulatory flavonoid genes.
Plant Physiol. 167 , 693-710, (2015) Trees in the genus Populus (poplar) contain phenolic secondary metabolites including the proanthocyanidins (PAs), which help to adapt these widespread trees to diverse environments. The transcriptional activation of PA biosynthesis in response to herbivory an... |
|
|
In vivo chemical and structural analysis of plant cuticular waxes using stimulated Raman scattering microscopy.
Plant Physiol. 168 , 18-28, (2015) The cuticle is a ubiquitous, predominantly waxy layer on the aerial parts of higher plants that fulfils a number of essential physiological roles, including regulating evapotranspiration, light reflection, and heat tolerance, control of development, and provi... |
|
|
The Mitochondrial Protein Import Component, TRANSLOCASE OF THE INNER MEMBRANE17-1, Plays a Role in Defining the Timing of Germination in Arabidopsis.
Plant Physiol. 166(3) , 1420-35, (2014) In Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), small gene families encode multiple isoforms for many of the components of the mitochondrial protein import apparatus. There are three isoforms of the TRANSLOCASE OF THE INNER MEMBRANE17 (Tim17). Transcriptome analysis i... |
|
|
The WRKY45-Dependent Signaling Pathway Is Required For Resistance against Striga hermonthica Parasitism.
Plant Physiol. 168 , 1152-63, (2015) The root hemiparasite witchweed (Striga spp.) is a devastating agricultural pest that causes losses of up to $1 billion US annually in sub-Saharan Africa. Development of resistant crops is one of the cost-effective ways to address this problem. However, the m... |
|
|
Overexpression of Arabidopsis Ceramide Synthases Differentially Affects Growth, Sphingolipid Metabolism, Programmed Cell Death, and Mycotoxin Resistance.
Plant Physiol. 169 , 1108-17, (2015) Ceramide synthases catalyze an N-acyltransferase reaction using fatty acyl-coenzyme A (CoA) and long-chain base (LCB) substrates to form the sphingolipid ceramide backbone and are targets for inhibition by the mycotoxin fumonisin B1 (FB1). Arabidopsis (Arabid... |
|
|
Knocking Down of Isoprene Emission Modifies the Lipid Matrix of Thylakoid Membranes and Influences the Chloroplast Ultrastructure in Poplar.
Plant Physiol. 168 , 859-70, (2015) Isoprene is a small lipophilic molecule with important functions in plant protection against abiotic stresses. Here, we studied the lipid composition of thylakoid membranes and chloroplast ultrastructure in isoprene-emitting (IE) and nonisoprene-emitting (NE)... |