| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
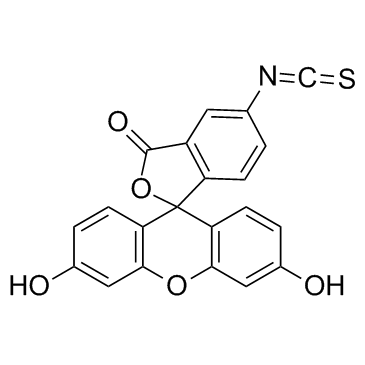 |
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
CAS:3326-32-7 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
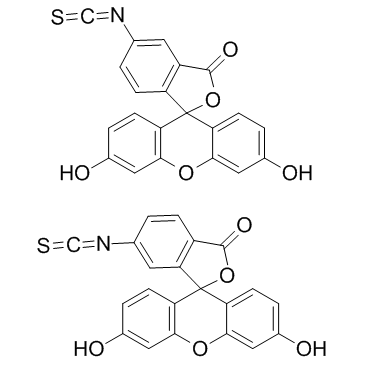 |
fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate
CAS:27072-45-3 |
|
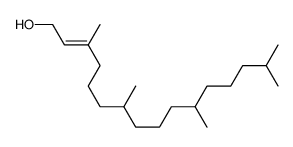 |
(Z,E)-phytol
CAS:7541-49-3 |
|
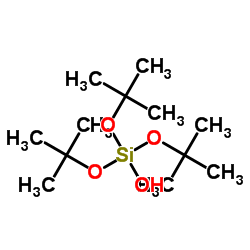 |
Tris(2-methyl-2-propanyl) hydrogen orthosilicate
CAS:18166-43-3 |
|
 |
Purine
CAS:120-73-0 |