AP-5 LITHIUM SALT
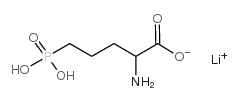
AP-5 LITHIUM SALT structure
|
Common Name | AP-5 LITHIUM SALT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 125229-62-1 | Molecular Weight | 203.05900 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11LiNO5P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Anatomical and electrophysiological changes in striatal TH interneurons after loss of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway.
Brain Struct. Funct. 220(1) , 331-49, (2015) Using transgenic mice that express enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) under the control of the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) promoter, we have previously shown that there are approximately 3,000 striatal EGFP-TH interneurons per hemisphere in mice. Here, w... |
|
|
A functional coupling between extrasynaptic NMDA receptors and A-type K+ channels under astrocyte control regulates hypothalamic neurosecretory neuronal activity.
J. Physiol. 592(Pt 13) , 2813-27, (2014) Neuronal activity is controlled by a fine-tuned balance between intrinsic properties and extrinsic synaptic inputs. Moreover, neighbouring astrocytes are now recognized to influence a wide spectrum of neuronal functions. Yet, how these three key factors act i... |
|
|
Histone deacetylase 3 inhibition re-establishes synaptic tagging and capture in aging through the activation of nuclear factor kappa B.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 16616, (2015) Aging is associated with impaired plasticity and memory. Altered epigenetic mechanisms are implicated in the impairment of memory with advanced aging. Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) is an important negative regulator of memory. However, the role of HDAC3 in ag... |
|
|
Enhanced lateral inhibition in the barrel cortex by deletion of phospholipase C-related catalytically inactive protein-1/2 in mice.
Pflugers Arch. 467 , 1445-56, (2015) We previously demonstrated that the deletion of phospholipase C-related catalytically inactive protein-1/2 (PRIP-1/2) enhances the desensitization of GABAA receptors (GABAARs), while it facilitates their resensitization at the offset of GABA puff, causing a h... |
|
|
Zolpidem and eszopiclone prime α1β2γ2 GABAA receptors for longer duration of activity.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172 , 3522-36, (2015) GABAA receptors mediate neuronal inhibition in the brain. They are the primary targets for benzodiazepines, which are widely used to treat neurological disorders including anxiety, epilepsy and insomnia. The mechanism by which benzodiazepines enhance GABAA re... |
|
|
PAR1-activated astrocytes in the nucleus of the solitary tract stimulate adjacent neurons via NMDA receptors.
J. Neurosci. 35(2) , 776-85, (2015) Severe autonomic dysfunction, including the loss of control of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and gastrointestinal systems, is a common comorbidity of stroke and other bleeding head injuries. Previous studies suggest that this collapse of autonomic control ... |
|
|
Lambert-Eaton syndrome IgG inhibits transmitter release via P/Q Ca2+ channels.
Neurology 84(6) , 575-9, (2015) To determine whether immunoglobulin G (IgG) from patients with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) decreases action potential–evoked synaptic vesicle exocytosis,and whether the effect is mediated by P/Q-type voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs).IgG was... |
|
|
Time-dependent modulation of glutamate synapses onto 5-HT neurons by antidepressant treatment.
Neuropharmacology 95 , 130-43, (2015) Antidepressants, including the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are thought to exert their clinical effects by enhancing serotonin (5-HT) transmission. However, animal studies show that the full magnitude of this enhancement is reached only fo... |
|
|
Glycine transporter-1 controls nonsynaptic inhibitory actions of glycine receptors in the neonatal rat hippocampus.
J. Neurosci. 34(30) , 10003-9, (2014) Although functional glycinergic synapses have not been identified in the hippocampus, neurons in this area express Cl(-) permeable extrasynaptic glycine receptors (GlyRs). In experiments on CA3 pyramidal neurons on postnatal day 0-6 rat hippocampal slices, we... |
|
|
Neurotransmitter regulation of c-fos and vasopressin gene expression in the rat supraoptic nucleus.
Exp. Neurol. 219 , 212-22, (2009) Acute increases in plasma osmotic pressure produced by intraperitoneal injection of hypertonic NaCl are sensed by osmoreceptors in the brain, which excite the magnocellular neurons (MCNs) in the supraoptic nucleus (SON) and the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) i... |