| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
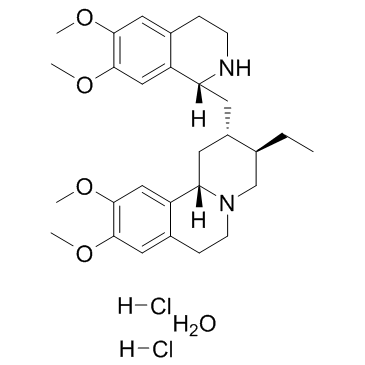 |
Emetine dihydrochloride hydrate
CAS:7083-71-8 |
|
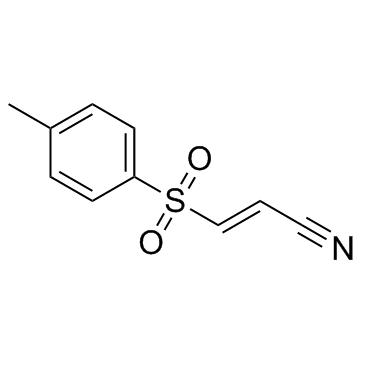 |
BAY 11-7082
CAS:19542-67-7 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
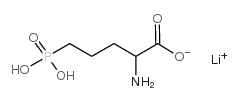 |
AP-5 LITHIUM SALT
CAS:125229-62-1 |
|
 |
DL-AP5
CAS:76326-31-3 |