| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Glycine
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
 |
4-AMINOPYRIDINE
CAS:504-24-5 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Glucose
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
Kynurenic acid
CAS:492-27-3 |
|
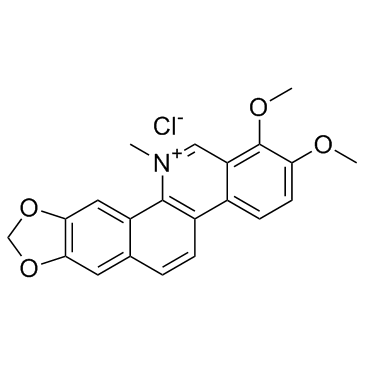 |
Chelerythrine chloride
CAS:3895-92-9 |
|
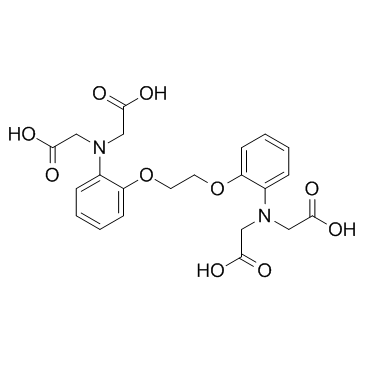 |
BAPTA
CAS:85233-19-8 |
|
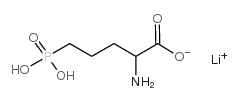 |
AP-5 LITHIUM SALT
CAS:125229-62-1 |
|
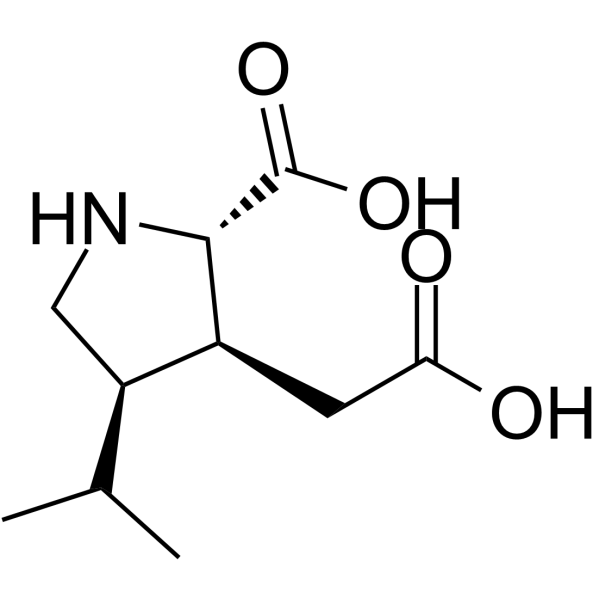 |
Dihydrokainic acid
CAS:52497-36-6 |