Nε,Nε,Nε-Trimethyllysine chloride
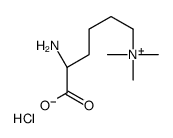
Nε,Nε,Nε-Trimethyllysine chloride structure
|
Common Name | Nε,Nε,Nε-Trimethyllysine chloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 55528-53-5 | Molecular Weight | 224.72800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H21ClN2O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Inhibition of histone binding by supramolecular hosts.
Biochem. J. 459(3) , 505-12, (2014) The tandem PHD (plant homeodomain) fingers of the CHD4 (chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 4) ATPase are epigenetic readers that bind either unmodified histone H3 tails or H3K9me3 (histone H3 trimethylated at Lys⁹). This dual function is necessary for ... |
|
|
A new type of protein lysine methyltransferase trimethylates Lys-79 of elongation factor 1A.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 455(3-4) , 382-9, (2014) The elongation factors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are extensively methylated, containing a total of ten methyllysine residues. Elongation factor methyltransferases (Efm1, Efm2, Efm3, and Efm4) catalyze at least four of these modifications. Here we report the... |
|
|
Tuning HP1α chromodomain selectivity for di- and trimethyllysine.
ChemBioChem. 12(18) , 2786-90, (2011) Histone lysine methylation is a critical marker for controlling gene expression. The position and extent of methylation (mono-, di-, or tri-) controls the binding of effector proteins that determine whether the associated DNA is expressed or not. Dysregulatio... |
|
|
Biosynthesis of proteins containing modified lysines and fluorescent labels using non-natural amino acid mutagenesis.
J. Biosci. Bioeng. 111(4) , 402-7, (2011) The preparation of posttranslationally modified proteins is required to investigate the function and structure of modified proteins. However, homogeneously modified proteins are not easily isolated from natural sources or prepared using modification enzymes. ... |
|
|
Treatment with pharmacological peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha agonist clofibrate causes upregulation of organic cation transporter 2 in liver and small intestine of rats.
Pharmacol. Res. 56(2) , 175-83, (2007) Activation of PPARalpha by clofibrate has recently been shown to cause upregulation of carnitine transporter organic cation transporter (OCTN) 2 and elevated carnitine concentrations in rat liver. The present study has been conducted to further explore the ef... |
|
|
Catalytic roles for carbon-oxygen hydrogen bonding in SET domain lysine methyltransferases.
J. Biol. Chem. 281(28) , 19280-7, (2006) SET domain enzymes represent a distinct family of protein lysine methyltransferases in eukaryotes. Recent studies have yielded significant insights into the structural basis of substrate recognition and the product specificities of these enzymes. However, the... |
|
|
Methyl group migration during the fragmentation of singly charged ions of trimethyllysine-containing peptides: precaution of using MS/MS of singly charged ions for interrogating peptide methylation.
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 20(6) , 1172-81, (2009) Core histones are susceptible to a range of post-translational modifications (PTMs), including acetylation, phosphorylation, methylation, and ubiquitination, which play important roles in the epigenetic control of gene expression. Here, we observed an unusual... |
|
|
Purification and assay protocols for obtaining highly active Jumonji C demethylases
Anal. Biochem. 420(1) , 48-53, (2012) Jumonji C (JmjC) lysine demethylases (KDMs) are Fe(II)-dependent hydroxylases that catalyze the oxidative demethylation of methyllysine residues in histones and nonhistone proteins. These enzymes play vital roles in regulating cellular processes such as gene ... |
|
|
Recognition of trimethyllysine by a chromodomain is not driven by the hydrophobic effect.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104(27) , 11184-8, (2007) Posttranslational modifications of histone proteins regulate gene expression via complex protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions with chromatin. One such modification, the methylation of lysine, has been shown to induce binding to chromodomains in an aro... |
|
|
Kinetic manifestation of processivity during multiple methylations catalyzed by SET domain protein methyltransferases.
Biochemistry 46(12) , 3905-15, (2007) Processive versus distributive methyl group transfer was assessed for pea Rubisco large subunit methyltransferase, a SET domain protein lysine methyltransferase catalyzing the formation of trimethyllysine-14 in the large subunit of Rubisco. Catalytically comp... |